ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV) - Know How to Foster Stakeholder Relationship
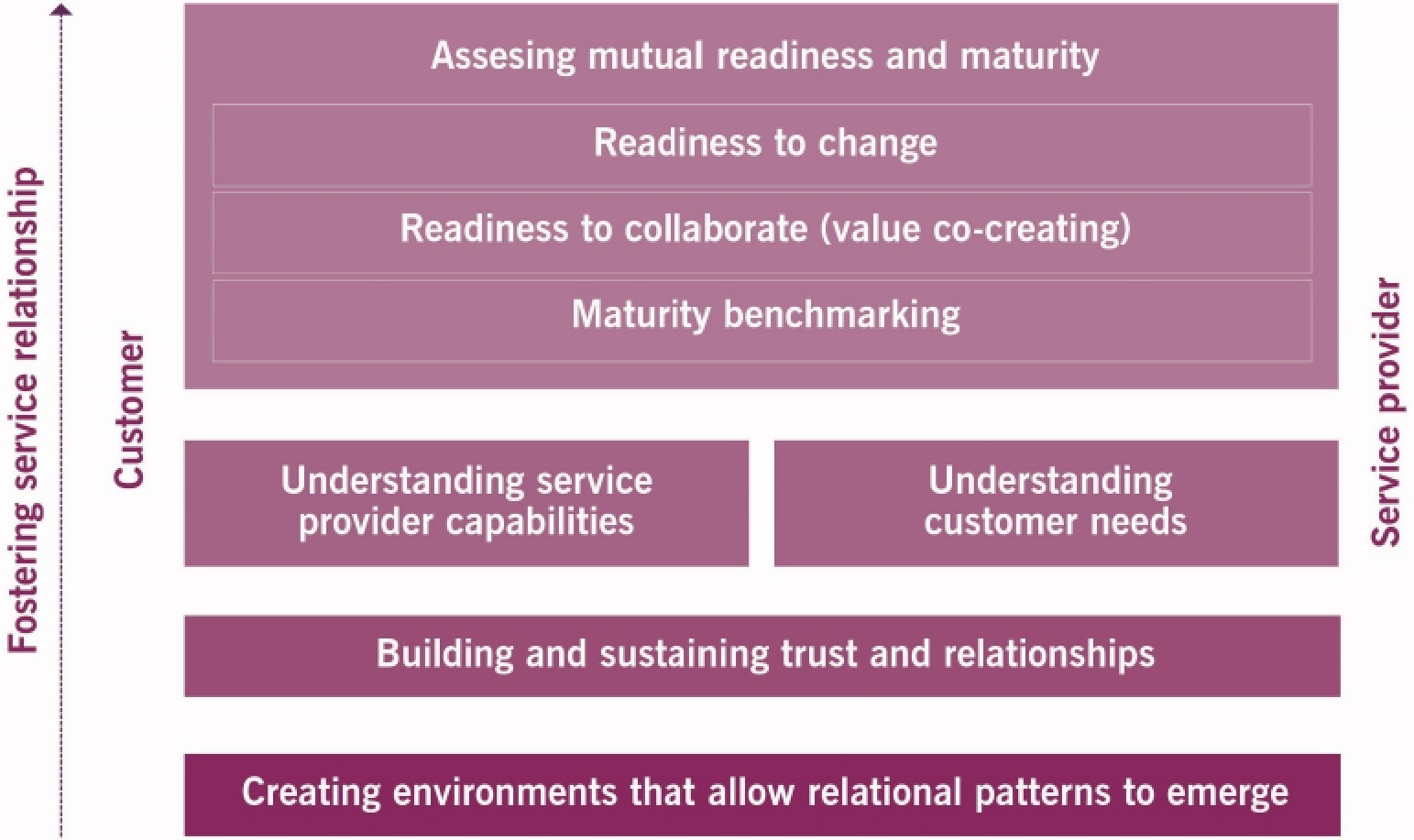
1. Mutual Readiness and Maturity
Context (explore first):
- Create environment that allows relational patterns to emerge
- Build and sustain trust and relationship
- Understand service provider capabilities
- Understand customer needs
Then assess mutual readiness and maturity
Remember: this is all part of engage, before we offer, negotiate and agree
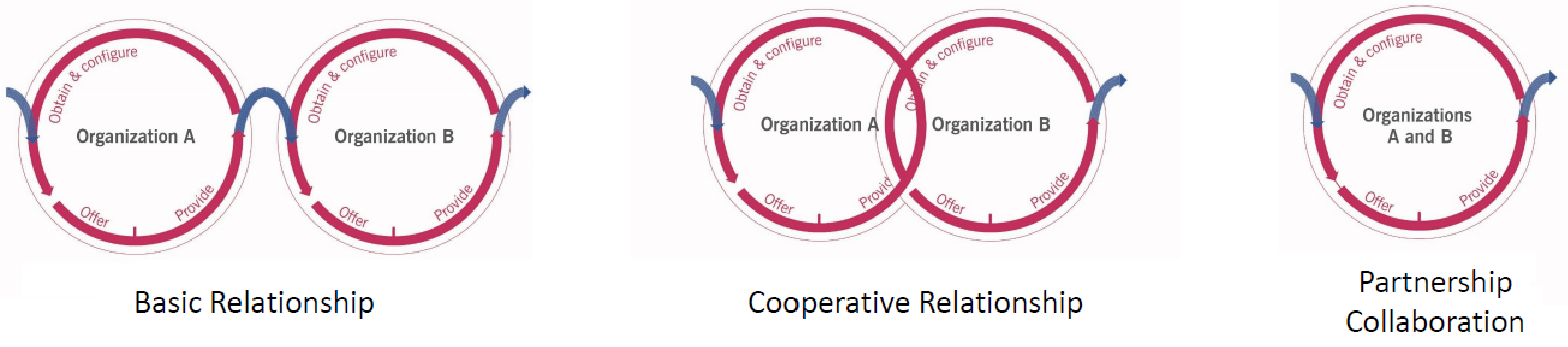
Assess once service provider capabilities and needs of customer are known; the exact assessment needed depends on the relationship type:
| Basic relationship | Cooperative relationship | Partnership | |
| Capabilities, maturity, and past performance (service provider) | Crucial | Moderate | Minor |
| Readiness to collaborate (both) | n/a | Moderate | Crucial |
| Readiness to change (customer) | n/a | Moderate | Crucial |
2. Managing supplier and partner relationships
Every organization depends on services provided by other organizations. Supplier and partner relationships are just as important as service provider and consumer
Service provider acts as the consumer in the relationship with the supplier: follows same steps of the customer journey (explore, engage, offer, agree, onboard, co‐create, realize)
Acting as a service integrator: use supplier management practice (org as SIAM, single supplier, service guardian, separate service integrator)
3. Service relationship types
| Basic relationship | Cooperative relationship | Partnership | |
| Relationship Maturity | Ad hoc, order taker Demand is prioritized based on weak or subjective data Frequent misperceptions build distrust The service provider is reactive and does not challenge customer requests There is a lack of quality data to support cost or value analyses |
Service provider, trusted adviser There is a mutual understanding and appreciation of demand and supply The service portfolio is appropriate to service consumer needs The service provider engages early and often in the customer decision cycle, and there is a shared understanding of product and service value |
Strategic partner The service provider and service consumer share common goals with a focus on value realization There is clear accountability for achieving value from investments in products and services and quality data to support value analysis |
| Approach for building a relationship | Loudest in, first out Frequent misperceptions may lead to distrust and reactive course changes, costs are usually transparent, but value may be hidden |
The routine is routine, but innovation is a challenge Collaboration is based on mutual respect and understanding Portfolio is aligned to service consumer demand |
Shared goals for maximizing value and shared risks and rewards |
| Key Attributes | Little information sharing Single channel of communication (dependent on single point of contact) Driven by price Easy to exit (usually a lot of alternative options) |
Service provider seeking opportunities to add value Many points of contact Forecasting, not joint planning Limited information sharing Expensive and resourceintensive |
Deep sense of trust and partnership Both acknowledge the importance of each other Streamlined process Wide range of jointly executed activities Free exchange of sensitive information Difficult to exit |
4. Develop customer relationships
Communicating and collaborating: listening modes (ignore, pretend, selective, attentive, empathetic)
Diversity:
- Cultural differences, time zones, seasonal factors, organizational culture…
- Foster respectful attitude, use correct language, safe environment for expression, take actions, continual align
5. Building service relationships
 |
 |
| Step | Customer status | Customer activities | Service provider activities |
| Awareness | Customer should be aware of the service/service provider |
Market research |
Marketing activities Facilitating effective connections |
| Motivation | Customer should be motivated to start a service relationship with service provider |
None |
Marketing activities Understanding alternatives Stimulate demand |
| Contacting | It should be easy for the customer to start a service relationship:
|
Contacting service provider Browsing service catalog |
Providing single point of contact Managing service catalog |
| Shaping expectation | Service provider should make the customer expect good experience |
Check past performance/public ratings of service provider Due diligence |
Aggregate and shape demand Ensure appropriate capacity and capabilities for service provision |
5.1 Three C’s of Trustworthiness
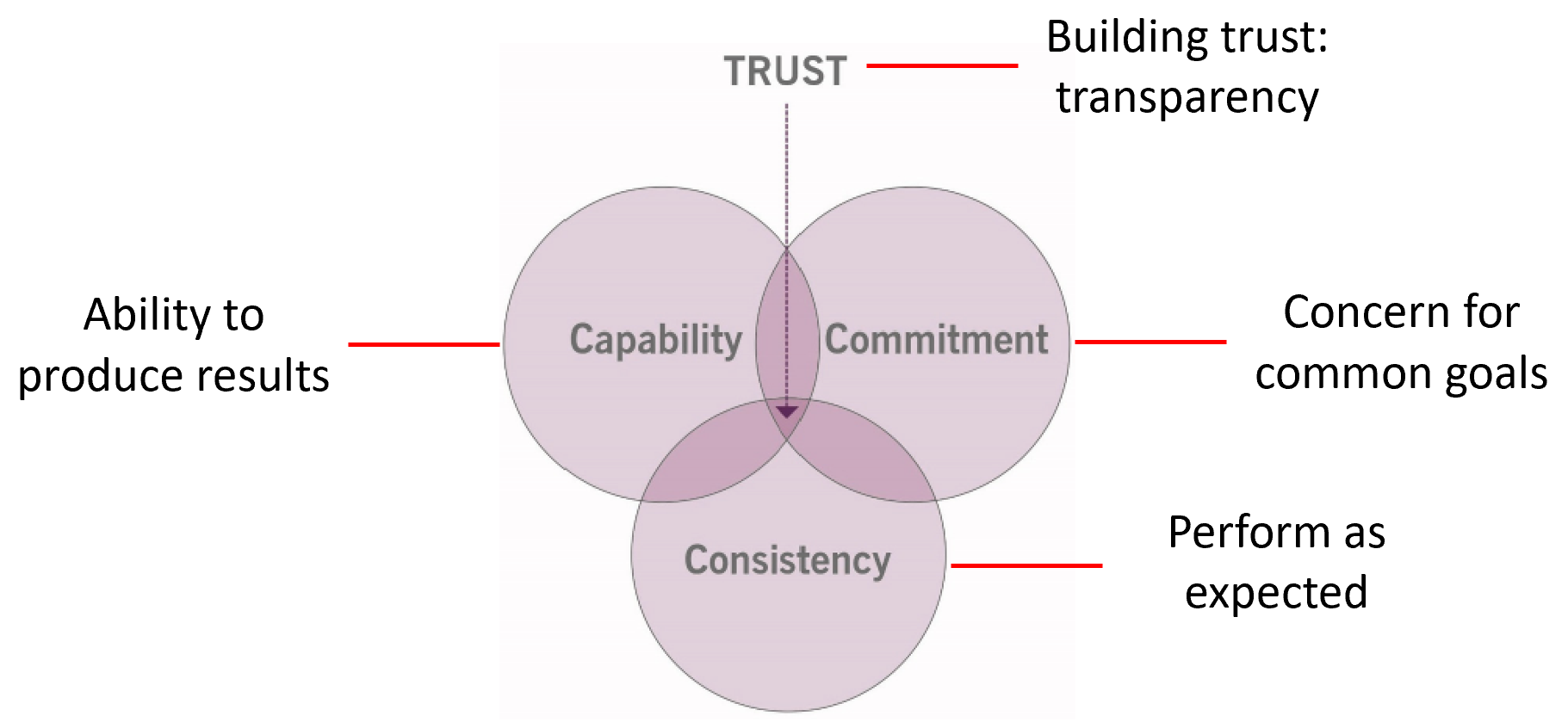
6. Service provider capabilities
Use the Four Dimensions to assess provider capabilities:
- Organization and people: duplication of activities, communication effectiveness, trust/transparency, type of org (centralized/decentralized), knowledge/learning culture, skills and competencies
- Information and technology: Current projects, integration, technical debt, tech trends, reliability of data, technical performance
- Partners and suppliers: Effective management of partners/suppliers, impact of key supplier shutdown, integration to value stream
- Value streams and processes: What processes in place and how they function, process performance, efficient management of value streams
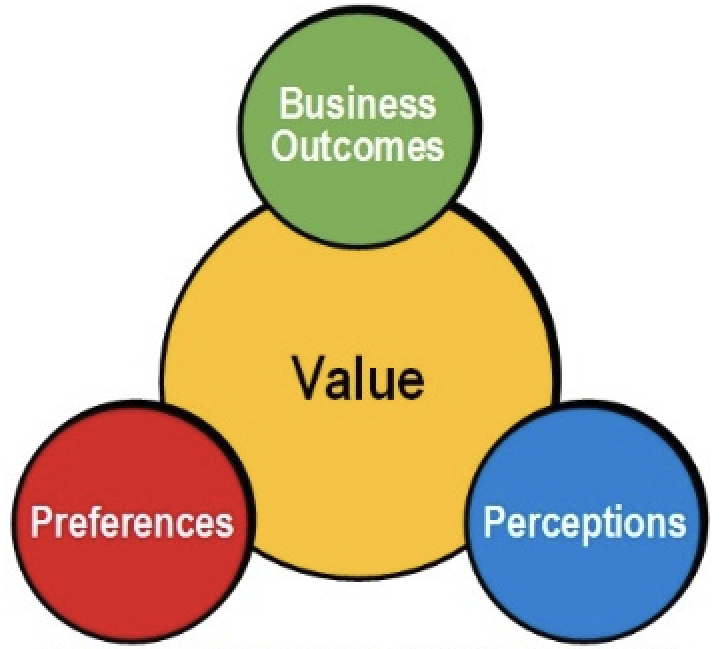
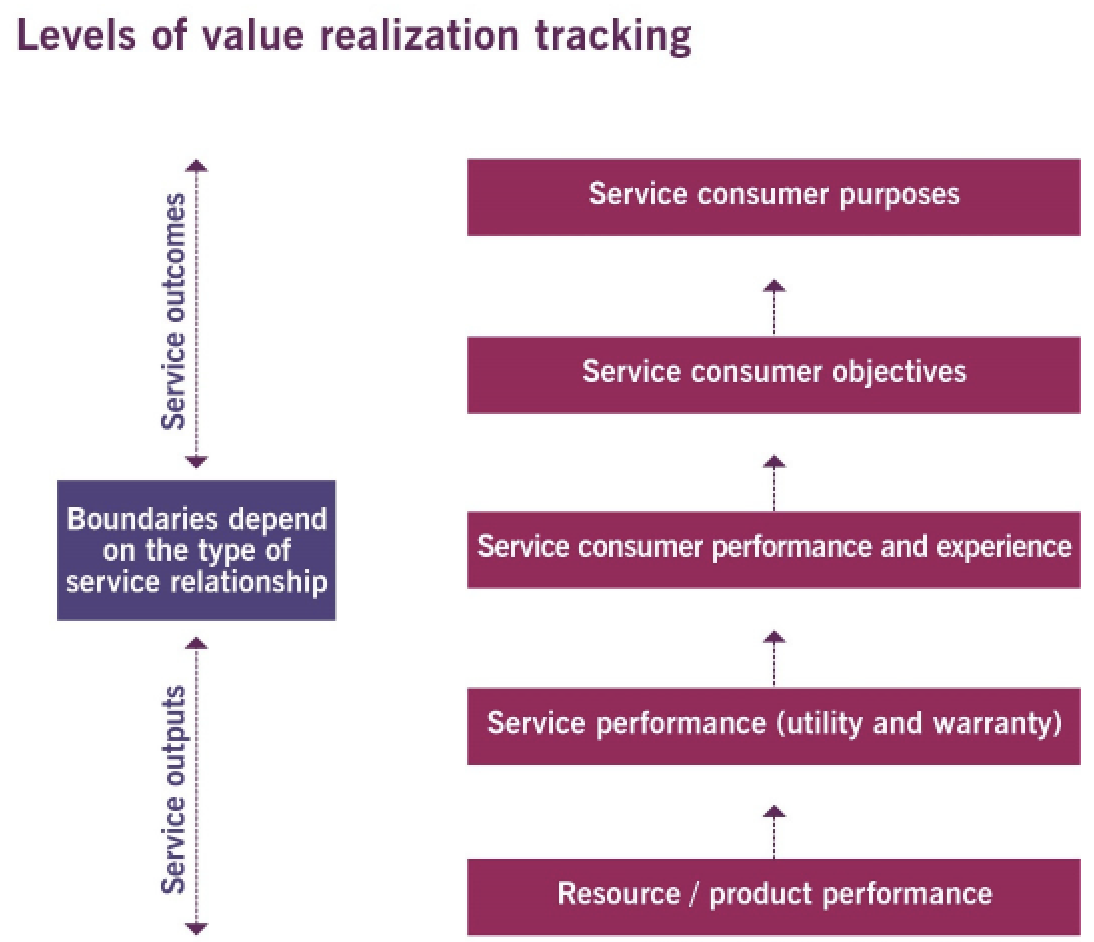
7. Understanding customer needs Customers do not buy services; they buy the fulfilment of particular needs:
Once outcomes, experiences, and preferences have been identified, the stakeholders can examine options for fulfilling the needs of the service consumer and making decisions |
 |
Go back to ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV) to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course.