ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV) - Shape Demand and Define Service Offerings
1. Designing digital service experiences
1.1 Lean
Process improvement philosophy
Prioritizes flow efficiency over resource efficiency
Terms:
- Flow
- Work unit
- Good flow
- Bad flow
| Principle | Explanation |
| Identify customer value | From the perspective of the customer, what are the needs/value/desired outcome ? |
| Map the value stream | Define the work unit and how it progresses through the value chain |
| Create flow | Eliminate waste |
| Establish pull | Optimize the value stream |
| Seek perfection | Continual improvement |
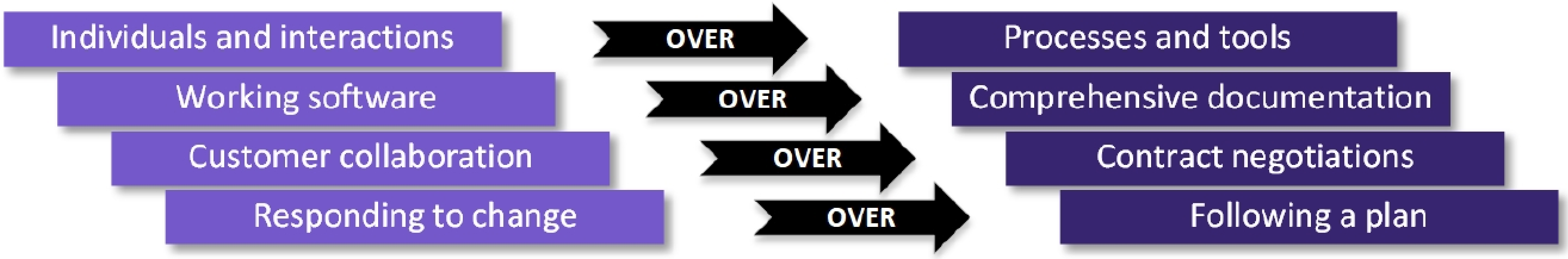
1.2 Agile
Manifesto for Agile Software Development: value in the items on the right but emphasizes the value of the items on the left more
Concept:
|
 |
Minimum viable product (MVP):
|
 |
1.3 Service design thinking Iterative design process: continuously gathering feedback on what works and what doesn’t Primary focus is on user experience (UX):
How designers should think to make innovative solutions that fit the needs of the users:
|



|
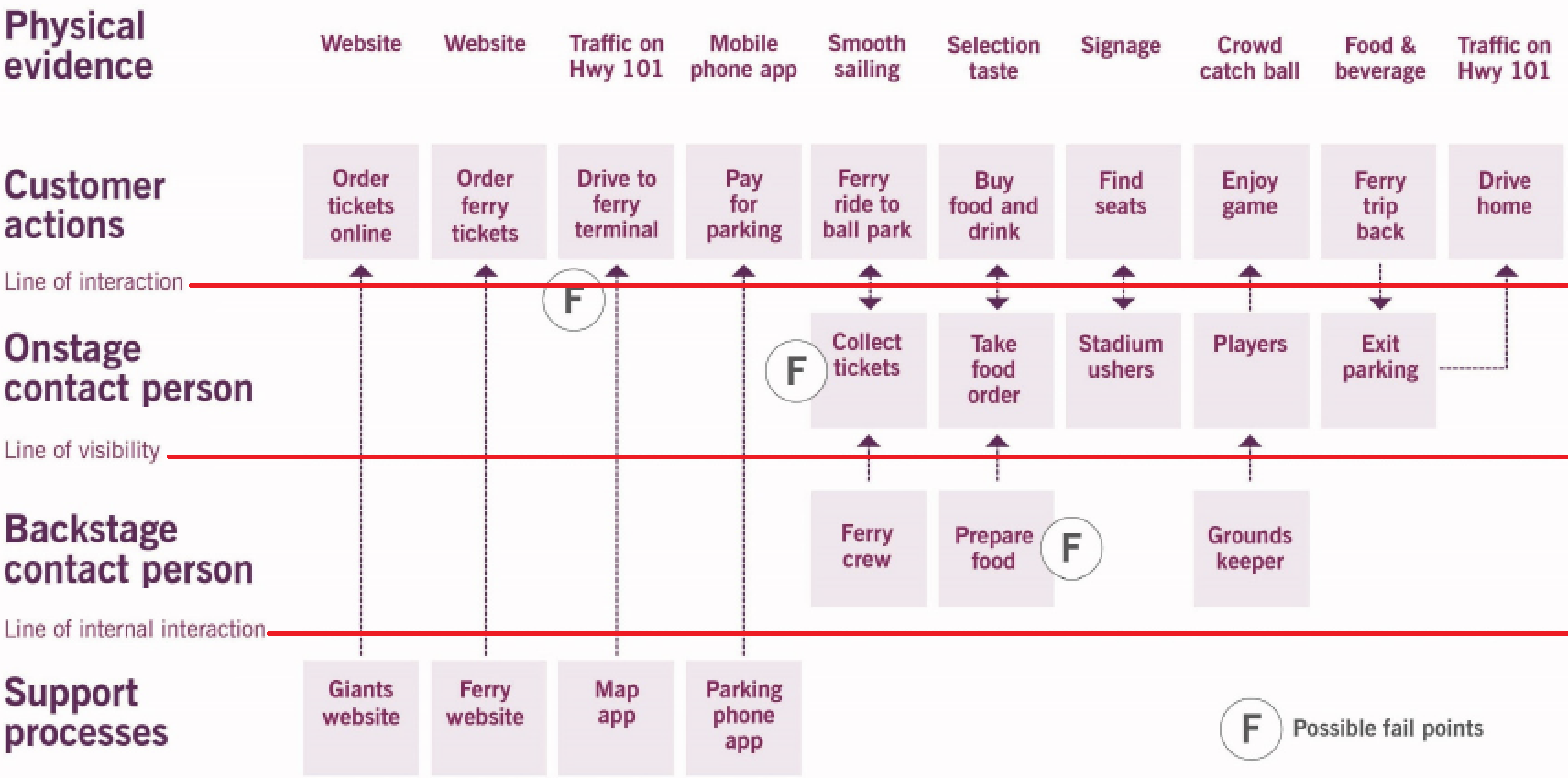
1.4 Service blueprinting
Key message: a service blueprint is a diagram visualizing the service usage, with the aim of optimizing the user experience. Key elements of the blueprint are:
- Line of interaction
- Line of visibility
- Line of internal interaction
One service can have multiple blueprints if there are different scenarios that it can support. Example service blueprint:
1.5 Design for onboarding
Include scope, actions, stakeholders, timelines, and other aspects of onboarding
Information may vary depending on the structure of service offerings, consumer resources, scale, legal and regulatory requirements, risks…
Use Four Dimension elements to guide scope and activities
Document the approach for onboarding with the Continual Improvement Model
Elements to include:
- Identify provider resources that will interact with consumer resources
- Identify consumer resources that will interact with provider resources
- Identify the need for introducing each pair of resources
- Explore opportunities to optimize and automate introductions
- Create procedures where manual or human‐controlled introduction is required
- Test the procedures and update based on test results (repeat as needed)
- Document and communicate to involved parties
2. Selling and procuring service offerings
Once products, services, service offerings have been designed, they need to be sold. Consider:
- Pricing
- Internal service relationships
- External service relationships
Don’t forget preferences, experiences, and outcomes influence the creation of value
2.1 Pricing
The service portfolio must generate enough income to cover investments, and costs (and generate profit, if appropriate)
Pricing and charging are different:
- Pricing: actual cost
- Charging: based on perceived value of service and costs of similar service from competitors
Options:
- Cost: break even or actual cost
- Cost plus: cost plus a set percentage
- Market price/going rate: comparable to similar service offerings
- Fixed price: fixed based on negotiation with customer (consumption)
- Differential charging: setting different charges based on time of usage
2.2 Internal sales
Raise awareness necessary to promote internal sales
Benefits of selling to internal customers:
- Better utilization of services
- Influence demand for services
- Improve communication with customers and users
- Achieve feedback on how well services meet needs
Supporting tools: Service catalogue, service desk, self‐help tools (can also use techniques used for external sales)
2.3 External sales
Use the traditional sales techniques: advertising and sales campaigns (good engagement, marketing, etc.)
Need good communication, trust, sense of fairness from both parties
Find a balance where both parties can win:
- Service provider (seek first to understand, then to be understood)
- Customer (describe requirements as needs, not detailed specifications)
Go back to ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV) to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course.
Interesting Topics
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Managing Professional
Study, study and study, I couldn’t be successfully certified without studying it, if you are interested...
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Strategic Leader
With my ITIL 4 Managing Professional certification (ITIL MP) in the pocket, it was time to go for the...
-

Hide visual and change background color based on selection
Some small tricks to customize the background colour of a text box...
-

Stacked and clustered column chart or double stacked column chart
In excel, I use a lot the combination of clustered and stacked chart...