ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV) - How to Realise and Validate Service Value
1. Service value
Value: the perceived benefits, usefulness, and importance of something
- Value proposition is a clear statement that explains how your product solves customers' problems or improves their situation (relevancy), delivers specific benefits (quantified value), tells the ideal customer why they should buy from you and not from the competition (unique differentiation)
- Value realization is showing the tangible or actual business value (quantifiable benefit) of an IT system or improvement
2. Realizing service value
| Basic relationship | Collaborative relationship | Partnership |
| Customer activities | If costs are low: no need to track If costs are high: basic value, outcome, cost, risk (VOCR) analysis based on assumptions and service provider reports |
Advanced VOCR analysis (e.g. side effects, risks, costs, benefits) based on agreement and promises |
| Shared activities | Ad-hoc service reviews |
Joint service reviews comparingachievements to expectations Joint analysis for improvement Occasional joint experimentation |
Continual tracking and analysis of outcomes, costs, and risks seeking optimization Sharing data and research Continual experimentation |
| Service provider activities | Report service outputs Provide access to analytics Internal provider: cost/risk control |
Sophisticated service level reports; analysis of customer outcomes; profitability/cost analysis; risk assessment; tracking and forecasting demand |
3. Tracking value realization
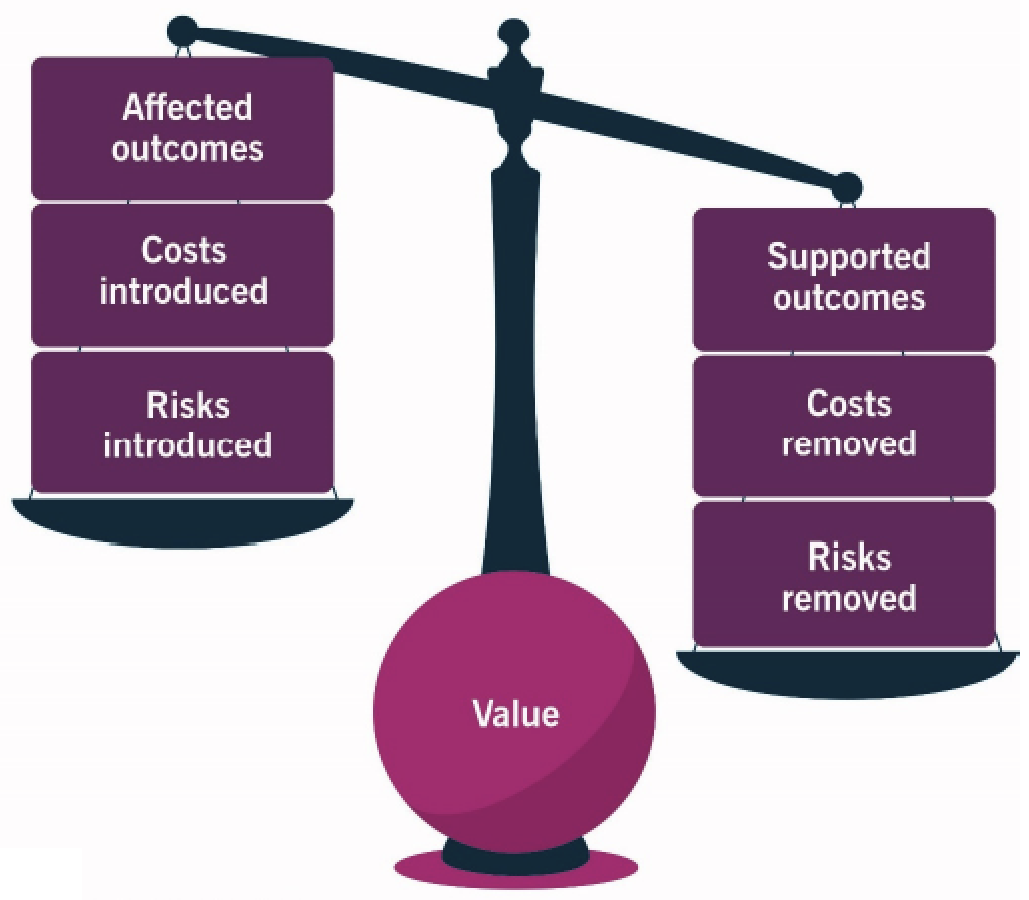
To assess and evaluate value realization, must track and measure service value indicators:
- Measure that directly or indirectly indicates the situation or level of a specific aspect of service value
- Indicators reflect achievement of an objective and are reinforced by metrics
To track value realization:
- Identify direct and indirect indicators of service value
- Define and measure underpinning metrics
- Capture measurement data
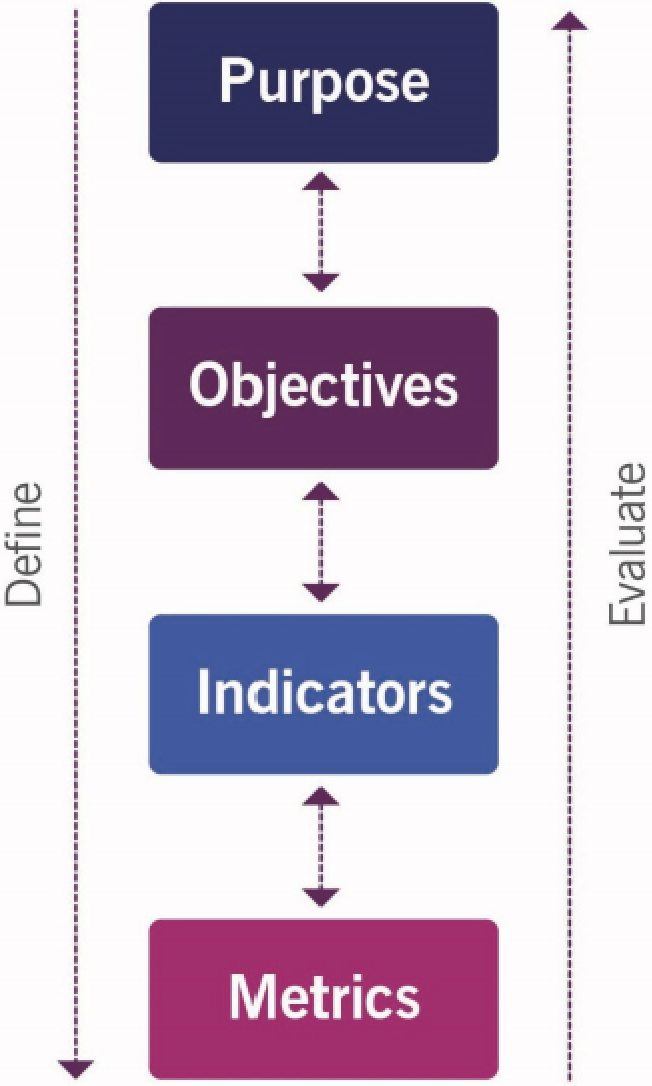
4. Track performance, output, and outcome
Hard to identify direct outcome indicators:
- Indirect outcomes (output and performance indicators) are easier
- Link the two to get an indirect service outcome
Use the value driver framework model:
- Lower layers are value drivers for higher layers
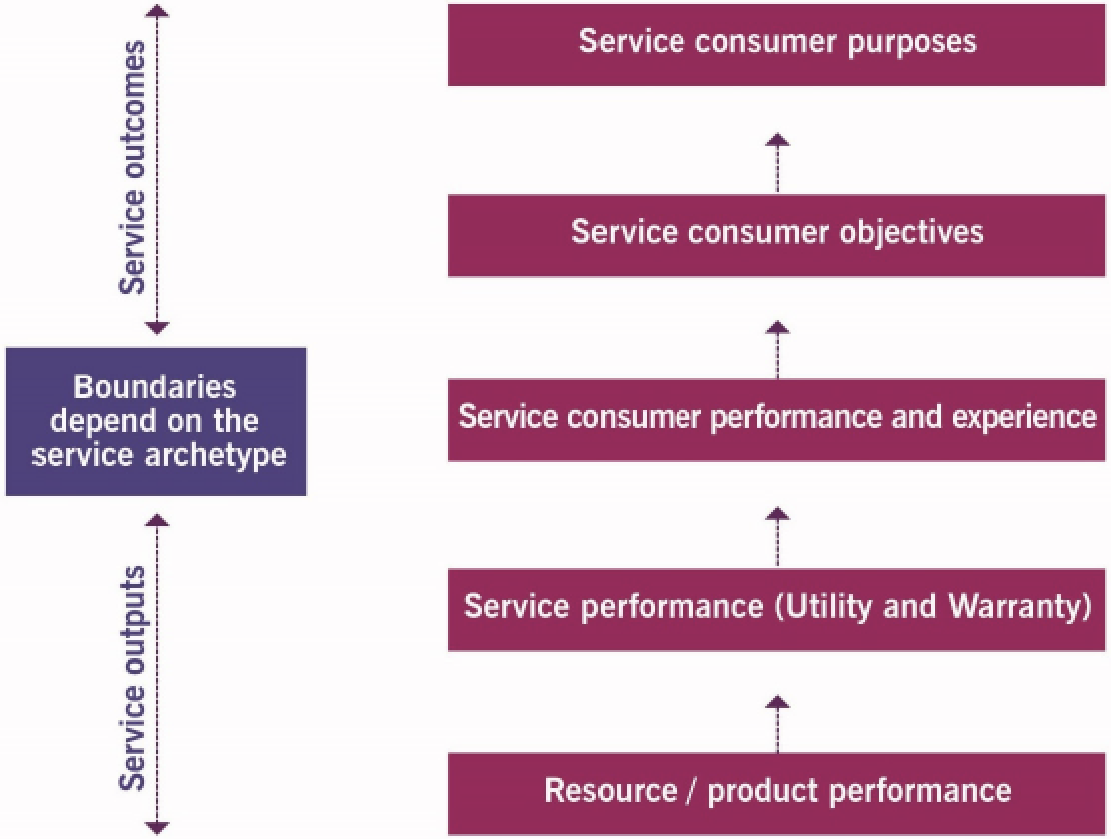
5. Measuring experience and satisfaction
5.1 Tracking experience and service usage
Methods to monitor customer experience:
- Customer feedback from service review meetings, major changes, releases…
- Monitoring social media
- Surveys/questionnaires (telephone perception surveys, feedback from post-implementation reviews, satisfaction surveys)
- Analysis of complaints and compliments
- A/B testing with focus groups
Tracking service usage:
- Use service metering and service usage analytics
- Patterns of business activity (PBA)
5.2 Tracking experience
Customer experience (CX): the sum of functional and emotional interactions with a service and service provider as perceived by a service consumer
Three questions:
- Functional experience: how does the service work ?
- Emotional experience: How does the service feel ?
- Satisfaction: How well does the service fulfill needs and expectations ?
| Experience criteria | Experience characteristic | Metrics |
| Functional experience: how does the service work ? | Uninterrupted completion of user actions | Number/frequency of user errors Frequency of using the back button Number/frequency of dropped service actions |
| Emotional experience: how does the service feel ? | Clear and convenient interface Effortlessness and speed of service actions |
Number/percentage of transactions where users used the interface help Average transaction handling time Customer effort score measurement First response rate User rating of service interface |
| Satisfaction: how well does the service fulfil needs and expectations ? | Functional and emotional experiences Loyalty to service provider |
Average and minimum rating that users give service Number/percentage of users that cancel subscription Customer churn rate Net promoter score |
6. Assess and report value realization
To assess and report on value realization, consolidate, correlate, interpret, present data from various data sources to enable decision-making (correlate experience, performance and output data with consumer outcomes, risks, costs, and impact to the customer objectives and purpose)
| Assessing and reporting outputs | Assessing and reporting outcomes | |
| Procedure | Relate data to agreed targets Combine data Report using agreed template/dashboard |
Consolidate data from many sources Link service outputs to objectives and purpose |
| Metrics aggregation and consolidation techniques | IT component to scorecard hierarchy | Organizational improvement cascade of similar |
| Assessment and reporting methods | SLA scorecard, service reviews Service level reports and dashboards SLM and Service financial management (cost data) |
ROI evaluation and/or cost benefit analysis Benchmarking; Post incident reviews, audits etc. Service financial management (cost data) |
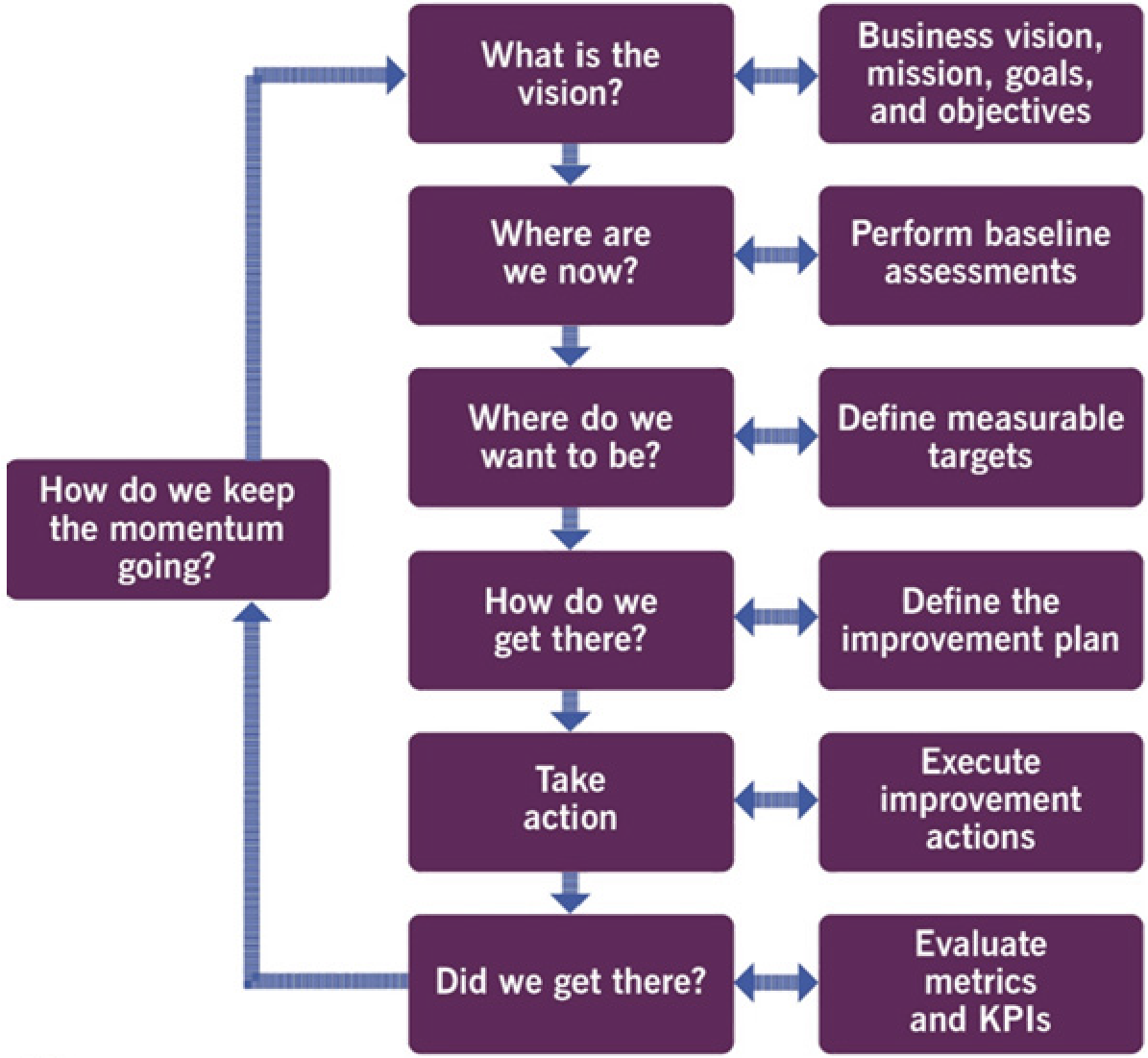
7. Evaluating and improving the customer journey
Steps 6 and 7 of the continual improvement model are required for value realization evaluation and improvement to customer journeys:
- Did we get there ?
- How do we keep the momentum going ?
- Note: be aware of and overcome recidivism (kotter; organizational change management)
8. Evaluation and verification of value realization
Simple environments, use service level targets, SLA scoreboards
Complex environments (much more difficult), use frequent service reviews, continual evaluation and negotiation of changes to the targets as well value measures may be required
Manage/challenge initial assumptions with these questions:
- Is there still a real problem that must be solved ?
- Is this service the best way to solve it ?
- Is the service still fit for purpose and fit for use ?
9. Continual improvement
Sources of improvement:
- Service usage analytics
- Incident, complaint, and problem analysis
- Analysis of service request patterns
- Analysis of self‐service patterns and usage of knowledge articles
- Change requests and improvement requests
- User feedback and feedback from user communities
- Customer feedback and customer satisfaction surveys
- Changes in service demand
10. Track, assess, evaluate outcomes
Internal service provider (ISP):
- Tied to the strategic goals of their legal entity
- Provider outcomes are directly related customer outcomes
External service provider (ESP):
- Pursues its own business goals though serves its customers and helps them achieve their goals
- ESP must track customer value realization but also its own value realization
11. Charging and billing
Charging policies define the cost recovery or profit:
- Cost recovery or break-even: only recover cost
- Recovery with a margin: recover more than cost (extra isn’t a profit but covers tech refresh or unanticipated costs)
- Cross-subsidization: charging an additional margin to cover the cost of another subset of services
- Customers who run out of budget, business performance lower than anticipated
- Risk that subsidies become permanent
- Profit: makes a profit for owners or reinvestment in the business
Cost allocation models used to develop charging:
- Enterprise cost allocation
- Service-based
- Activity-based
Define chargeable items (business view):
- Same as a cost unit (IT view)
- Lowest level at which a cost or charge is measured
Measuring service usage:
- Processor/memory/file storage utilization
- Transactional
- Requests
Billing options:
- No billing: no invoice; costs covered by enterprise cost allocation
- Informational (show‐back): produces invoice but no collection
- Internal billing (chargeback): receives a bill for charges directly related to customer use
- Billing and collection: dedication financial management system for invoicing, collection, debtors, creditors
Go back to ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV) to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course.
Interesting Topics
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Managing Professional
Study, study and study, I couldn’t be successfully certified without studying it, if you are interested...
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Strategic Leader
With my ITIL 4 Managing Professional certification (ITIL MP) in the pocket, it was time to go for the...
-

Hide visual and change background color based on selection
Some small tricks to customize the background colour of a text box...
-

Stacked and clustered column chart or double stacked column chart
In excel, I use a lot the combination of clustered and stacked chart...