ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Foundation - Key Definitions
Cost: the amount of money spent on a specific activity or resource
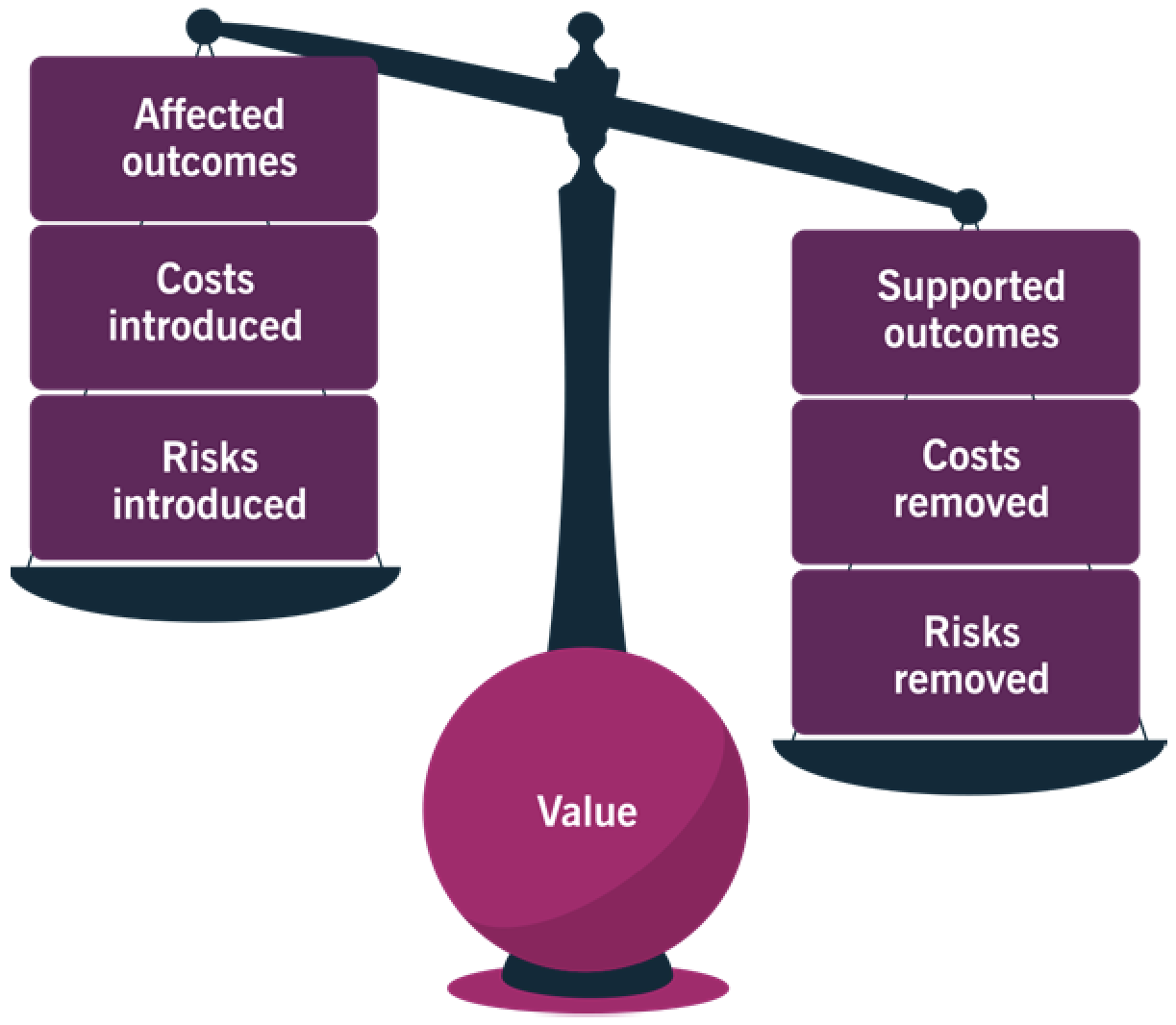
Criticality of Value: service relationships are perceived as valuable only when they have more positive effects than negative. Services:
- Enable value co-creation
- Facilitate outcomes
- Manage costs and risks
Customer: the role that defines the requirements for a service and takes responsibility for the outcomes of service consumption
Individual: an individual may fulfill all three roles (customer, user, and sponsor)
Organization: a person or a group of people that has its own functions with responsibilities, authorities and relationships to achieve its objectives
Outcome: a result for a stakeholder enabled by one or more outputs
Output: a tangible or intangible deliverable of an activity
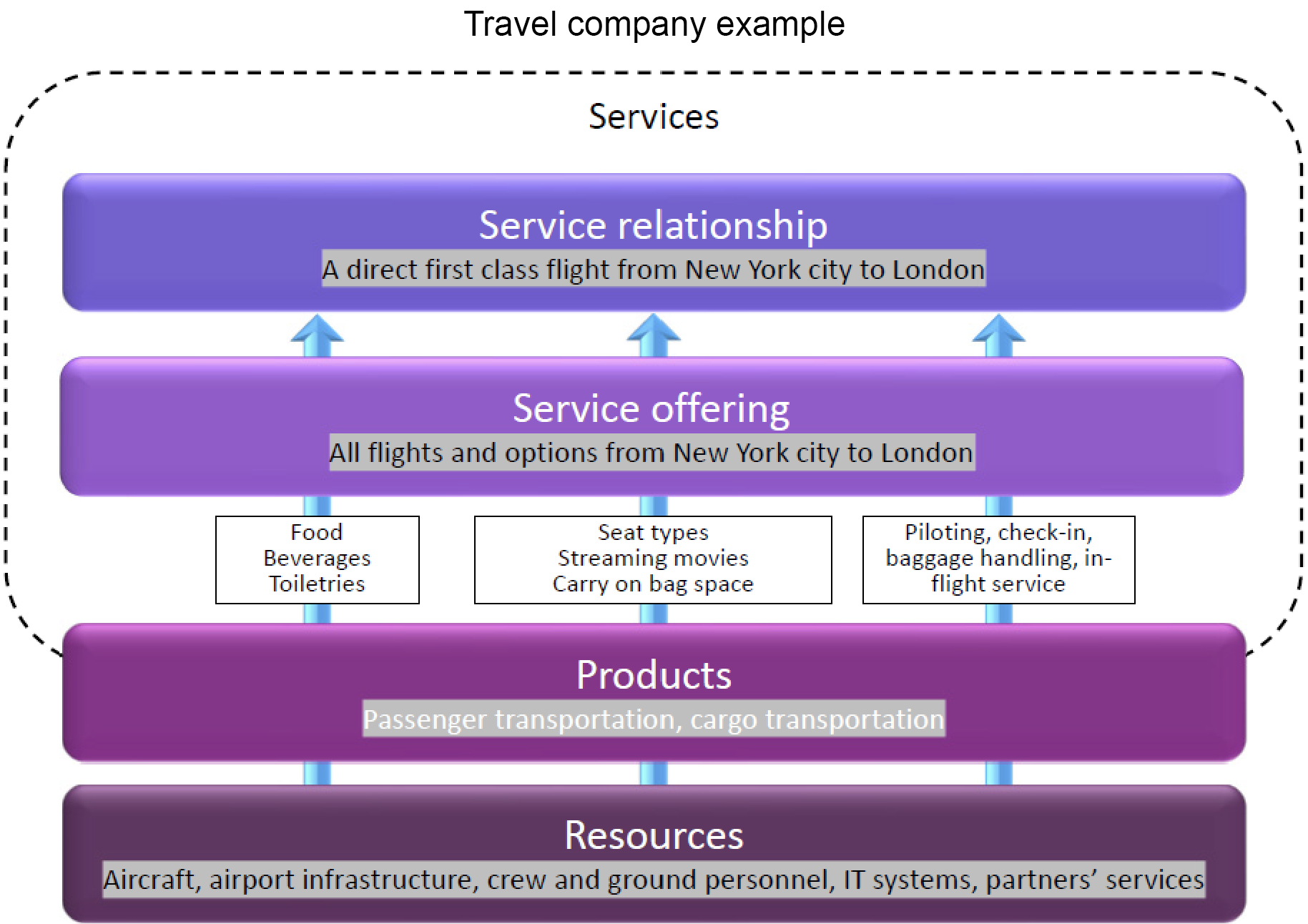
Product: a configuration of an organization’s resources designed to offer value for a consumer
Process: a set of interrelated or interacting activities that transform inputs to outputs (what):
- Describes what is done to accomplish an objective (sequence of actions and dependencies)
- Well‐defined processes improve productivity within/across an organization
- Supported by procedures (how) and work instructions (who)
Risk: a possible event that could cause harm or loss, or make it more difficult to achieve objectives. It can also be defined as uncertainty of outcome and can be used in the context of measuring the probability of positive outcomes as well as negative outcomes
Service: a means of enabling value co-creation, by facilitating outcomes that customers want to achieve, without the customer having to manage specific costs and risks
Service management: a set of specialized organizational capabilities for enabling value for customers in the form of services
Sponsor: the role that authorizes budget for service consumption. It can also be used to describe an organization or individual that provides financial or other support for an initiative
User: the role that uses services
Utility: the functionality offered by a product or service to meet a particular need
Value: the perceived benefits, usefulness, and importance of something
Value co-creation: active collaboration between providers and consumers, as well as other organizations that are part of the relevant service relationships
Value Stream: series of steps an organization uses to create and deliver products and services to a service customer (combination of the organization’s value chain activities)
Warranty: assurance that a product or service will meet agreed requirements
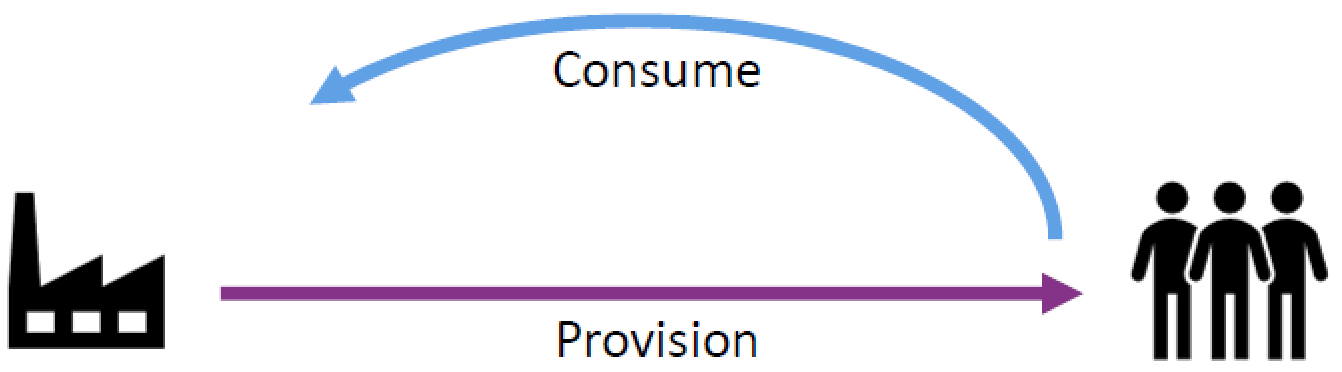
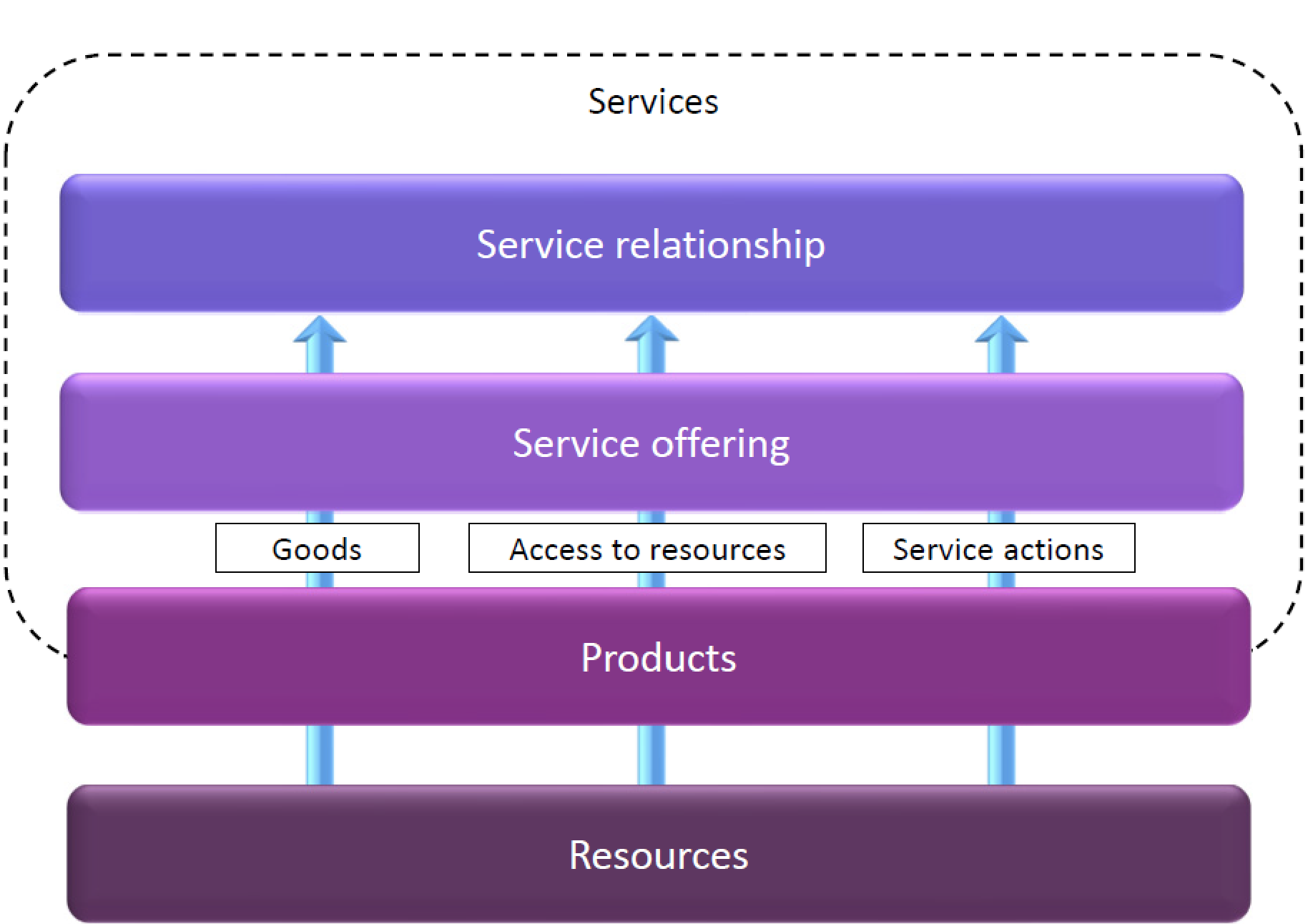
Service provision: activities performed by an organization to provide services including the management of resources, configured to deliver the service, access to these resources for users, fulfilment of the agreed service actions, service performance management and continual improvement. It may also include the supply of goods. Examples:
- Management of provider resources configured to deliver the service
- Provision of access to resources for users
- Fulfillment of the agreed service actions
- Service performance management and continual improve
Service consumption: activities performed by an organization to consume services including managing consumer’s resources needed to use the service, managing service actions by users (utilizing provider’s resources and requesting service actions to be fulfilled). It may include receiving (acquiring) goods. Examples: |
 |
- Management of the consumer resources needed to consume the service
- Utilization of the providers resources
- Requesting of service actions to fulfill
- Receipt of or acquiring goods
Service offering: a description of one or more services, designed to address the needs of a target consumer group. A service offering may include goods, access to resources, and service actions. Service providers present their services to consumers in the form of service offerings, which describe one or more services based on one or more products:
- Can be goods supplied to the consumer (consumer takes ownership and decides use)
- Access to resources granted or licensed to a consumer (terms and conditions)
- Service actions performed to address a consumer’s need
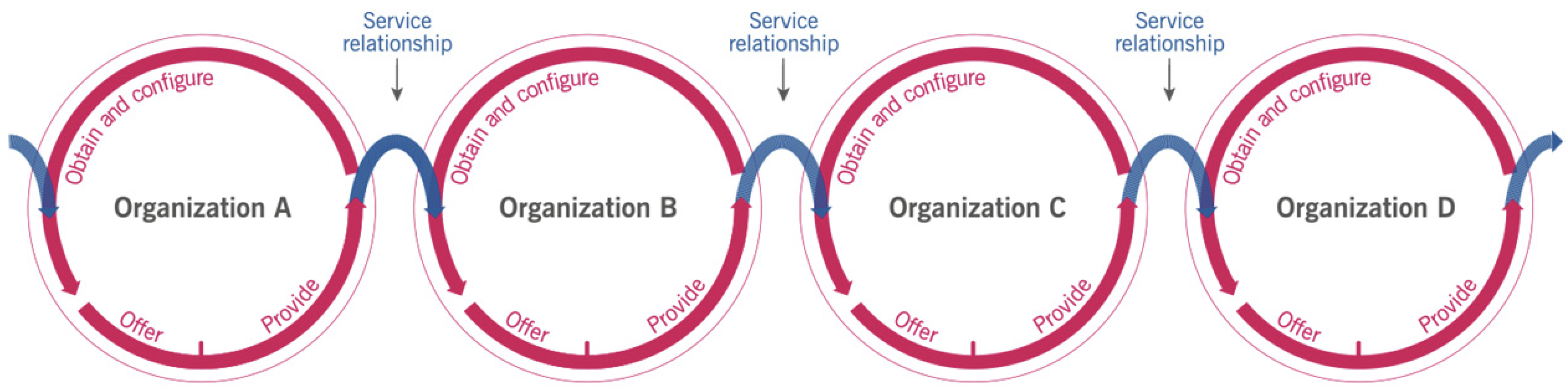
Service relationship management: joint activities performed by a service provider (service providers are also service consumers) and a service consumer to ensure continual value co-creation based on agreed and available service offerings. Service relationships are established between two or more organizations to co-create value:
- Service provisioning (providers)
- Service consumption (consumers)
 |
 |
Go back to ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Foundation to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course.
Interesting Topics
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Managing Professional
Study, study and study, I couldn’t be successfully certified without studying it, if you are interested...
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Strategic Leader
With my ITIL 4 Managing Professional certification (ITIL MP) in the pocket, it was time to go for the...
-

Hide visual and change background color based on selection
Some small tricks to customize the background colour of a text box...
-

Stacked and clustered column chart or double stacked column chart
In excel, I use a lot the combination of clustered and stacked chart...