ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Customer/Market Relevance - Strategic Approaches for Digital Organizations
1. Business models for strategy planning
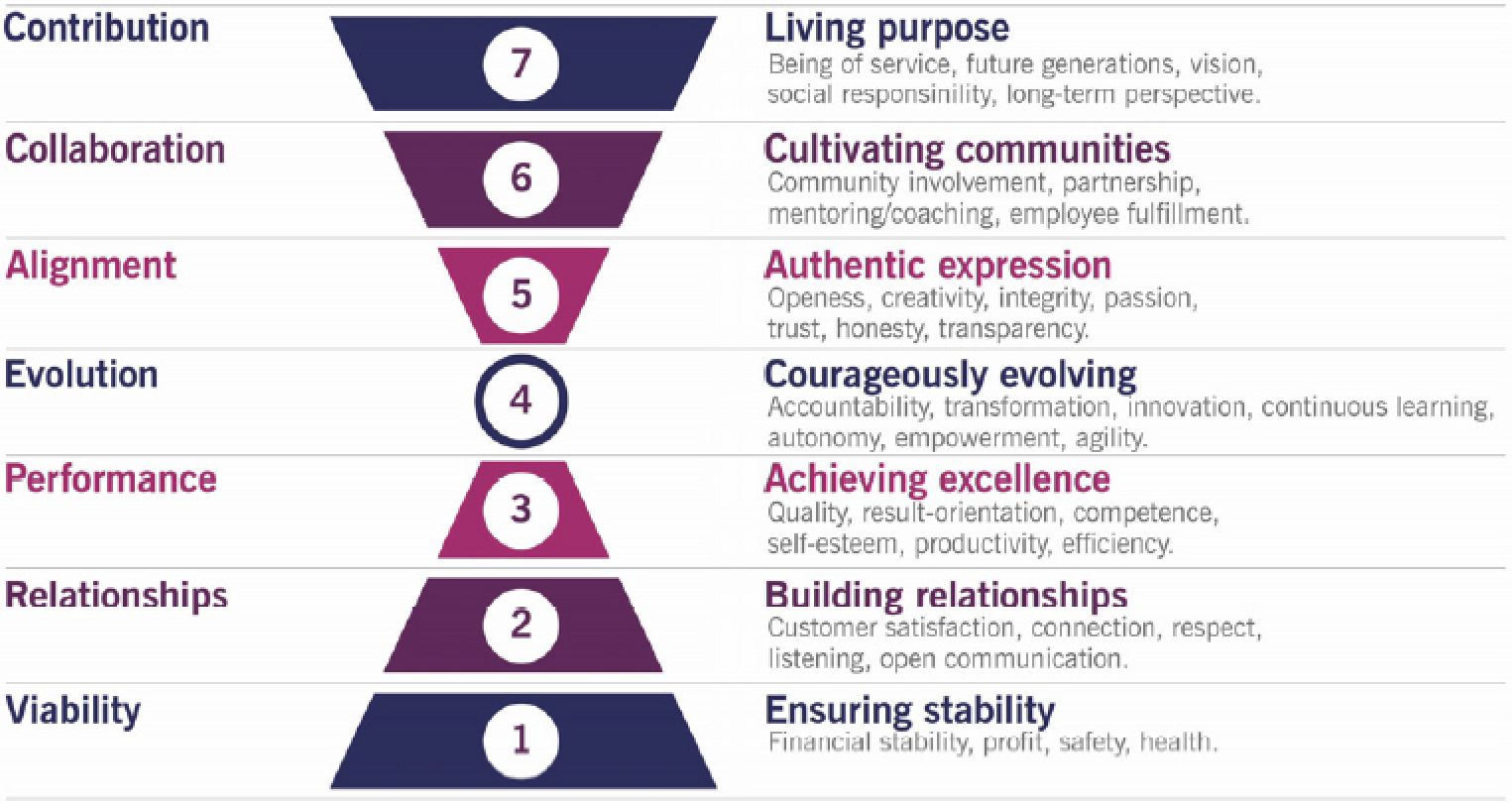
| Key values according to the Barrett model | Signs suggesting that the business model is being exploited or should evolve | Signs suggesting a need to protect or review the business model |
| Purpose (alignment/collaboration/contribution) | New needs of society New opportunities for collaboration and value co-creation |
New regulations challenging the business model Feedback indicating a decline in the value perceived by the stakeholders |
| Evolution (transformation) | Other external factors suggesting a need or opportunity to transform the business Innovative ideas being generated in the organization, suggesting a transformation opportunity |
External opportunities that cannot be used within the current business model Large-scale disasters affecting the relevance and viability of the current business model and strategy |
| Foundation (viability/relationships/performance) | Opportunity or a new business model due to new or emerging technology Removal of a barrier to entry for customers who were excluded from the existing market, by providing cheaper prices or simpler solutions |
A declining trend in performance metrics such as market value, customer retention, product or service sales, or customer satisfaction Difficulty in finding new ways to enhance offerings and value propositions for the current business model |
1.1 Focus of strategic approaches
| Levels of the Barrett model | Key foci of the strategic approaches |
| Purpose (levels 5-7: alignment, collaboration, contribution) | Social responsibility Sustainability Community involvement Transparency Employee fulfilment |
| Evolution (level 4: transformation) | Innovation Agility and resilience Organizational changes Knowledge and learning |
| Foundation (levels 1-3: viability, relationships, performance) | Customer/market relevance Operational excellence |
2. Evolution
Business models based on utilization of emerging opportunities need:
- Innovation
- Agility and resilience
- Embrace organizational change
- Develop new competencies (knowledge management)
2.1 Innovation
Innovation: the adoption of a novel technology or way of working that has led to the significant improvement of an organization, product, or service.
To be innovative, must increase/improve value outcome: technology, work methods do not guarantee success or innovation
Innovation can’t be managed but a small, subgroup of staff: must be imbedded in all aspects of the organization, if it is to a strategic initiative. Innovation opportunities are discovered via continually monitoring relevant sources and internal research/development work
Address innovation initiatives promptly:
- Involve the originators; create a level of transparency
- Create feedback loops
- Allow for failure
2.2 Agility and resilience
Organizational agility: an organization’s ability of to move and adapt quickly, flexibly, and decisively in response to events in the internal or external environment
Organizational resilience: an organization's ability to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and overcome adverse events in the internal or external environment
Organization’s mission and vision and subsequent business model manage the agility and resilience expected by stakeholders: Mmst know external factors (PESTLE) and organizational priorities and objectives to accurately develop resilience
2.3 OCM
Use OCM to develop a value-driven environment: must change people (behaviors), thus need the means/methods to do so
OCM reduces risks and negative impact of change on products, services, customer experience
To achieve effective and sustainable organizational changes, an organization should:
- Create and maintain a change-enabling culture across the organization
- Establish and maintain a holistic approach and continual improvement for organizational change management
- Ensure that organizational changes are realized in an effective manner, satisfying stakeholders’ needs and meeting compliance requirements
Principles to support OCM:
- Clear and relevant objectives
- Strong and committed leadership
- Willing and prepared participants
- Sustained improvement
2.4 Knowledge management
Continual professional development and knowledge management necessary for organizational evolution
Absorptive capacity: an organization’s ability to recognize the value of new information, embed it into an existing knowledge system, and apply it to achieve the business outcomes
To increase absorptive capacity:
- Create/use new knowledge to support innovation
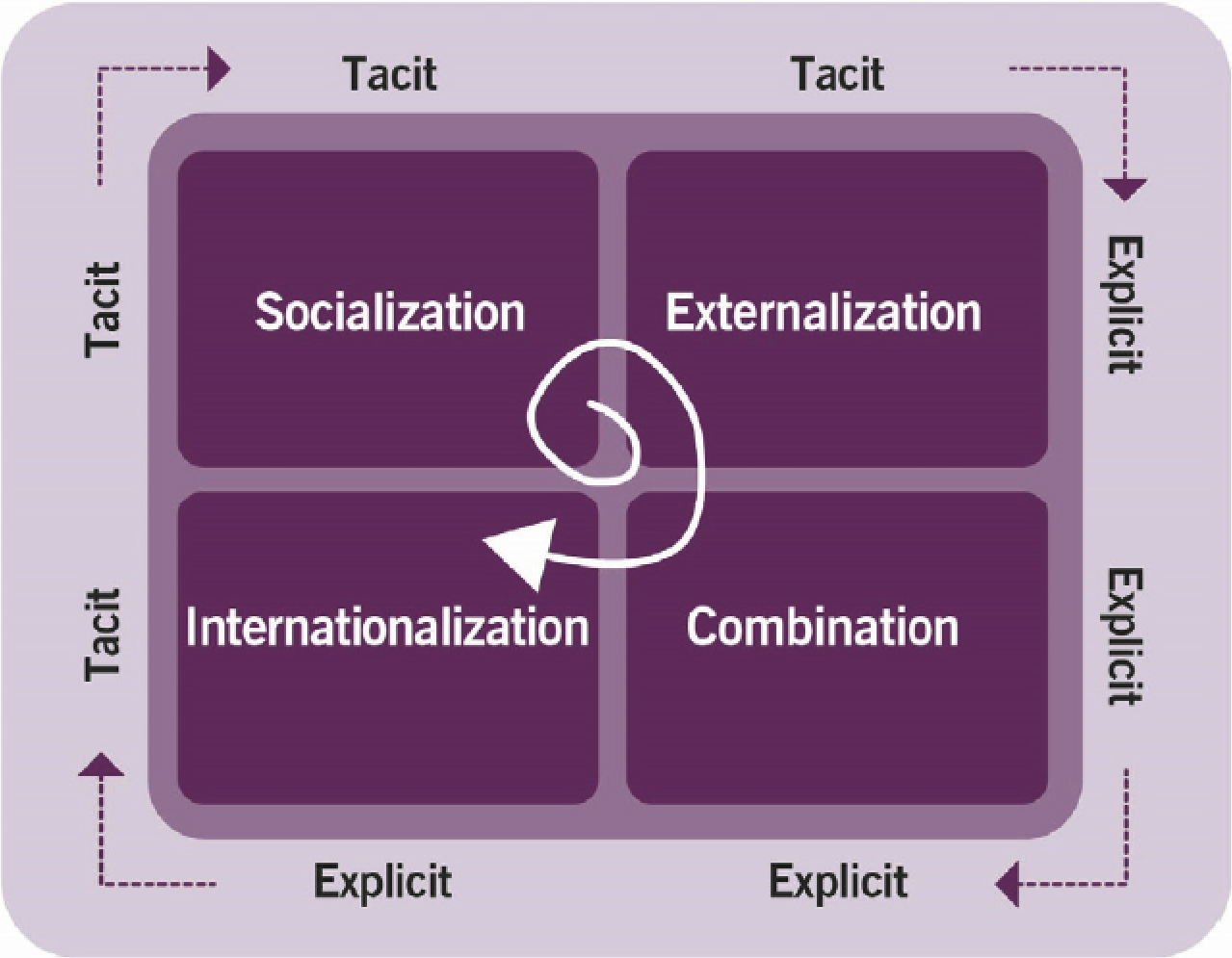
- SECI model:
- Explicit knowledge: transferrable to others, codified, assessed, verbalized, stored (books, databases, descriptions…)
- Tacit knowledge: difficult to transfer to others, to express, codify, or express; based on experience, values, capabilities, skills
- Model is based on the ability to convert tacit to explicit knowledge as well as from the individual to group
2.5 Social responsibility and sustainability
Sustainability: a business approach focused on creating long-term value for society and other stakeholders by addressing the risks and opportunities associated with economic, environmental, and social developments
Evolved from environmental factors to employee fulfillment (well-being, continuing development) and employee’s need for purpose:
- Triple bottom line
- Employee fulfillment
2.5.1 Triple bottom line
Traditional focus on profitability is being replaced with a focus on economic, social, and environmental factors
Sustainability as a strategic initiative:
- Embed in all teams, value streams, products, services
- Must have policies that are clearly defined and communicated and embedded in ArchM, SuppM, BusAnalysis, SFM, RelM, SerDes, PortM which become inputs to strategy definition

2.5.2 Employee fulfillment
Employee fulfillment: the feeling that people have when their work aligns with their intrinsic motivation and provides them with a sense of purpose
Develop the view that employees are stakeholders:
- Acquire and retain talent and drive innovation by meeting employee’s individual needs
- A focus on employees’ sense of purpose is a necessity
Provide opportunities that emphasize relationships, impact, growth:
- Meaningful work relationships
- How contributions are view
- Developing to overcome personal challenges
- Senior leadership, mangers, teammates…and the employee themselves can be seen as obstacles to employee fulfillment
Go back to ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Customer/Market Relevance to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course.
Interesting Topics
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Managing Professional
Study, study and study, I couldn’t be successfully certified without studying it, if you are interested...
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Strategic Leader
With my ITIL 4 Managing Professional certification (ITIL MP) in the pocket, it was time to go for the...
-

Hide visual and change background color based on selection
Some small tricks to customize the background colour of a text box...
-

Stacked and clustered column chart or double stacked column chart
In excel, I use a lot the combination of clustered and stacked chart...
-

Refresh Power BI
From the Power BI Service, I can set refresh but, for instance, there is no option to do it monthly or each time a change is made...
-

Power BI alerts to be sent by email from an excel file based on condition
I will explain how to send a list of emails from an excel file after creating alerts...