ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Customer/Market Relevance - Financial Aspects of DITS
Financial aspects must reflect/support organizational goals and customer needs: appropriate funding allows for successful business models, new/enhanced products/services taking into account conditions and needs
Agile vs. traditional organization funding strategies:
- Agile: break down funding into smaller budgets, allowing flexibility based on need, environment, market, customers (fund at team level and across value streams)
- Traditional: large, multi-year projects and programs (funds tied to projects where it could have been invested in other areas for more of an immediate return)
1. Financial policies
Capital costs: cost of purchasing or creating resources, which are recognized as financial assets (depreciation)
Operational costs: cost the organization incurs through its normal business operations
Financial growth is goal of many strategies; finances are required for most strategies
The most common financial policies are:
- Funding mix: the availability of funding for strategic initiatives depends largely on the appetite of those who will be investing in the strategy, and their perspective on the strategic options
- Planning for growth:
- Budgeting and funding practices must align to the level of agility or flexibility required by the strategy
- These strategies use scenario planning and Service Models that show how spending will vary in different situations
- Tax-based strategies: large corporations may base their strategy on which countries provide the best tax advantages for which type of business activity
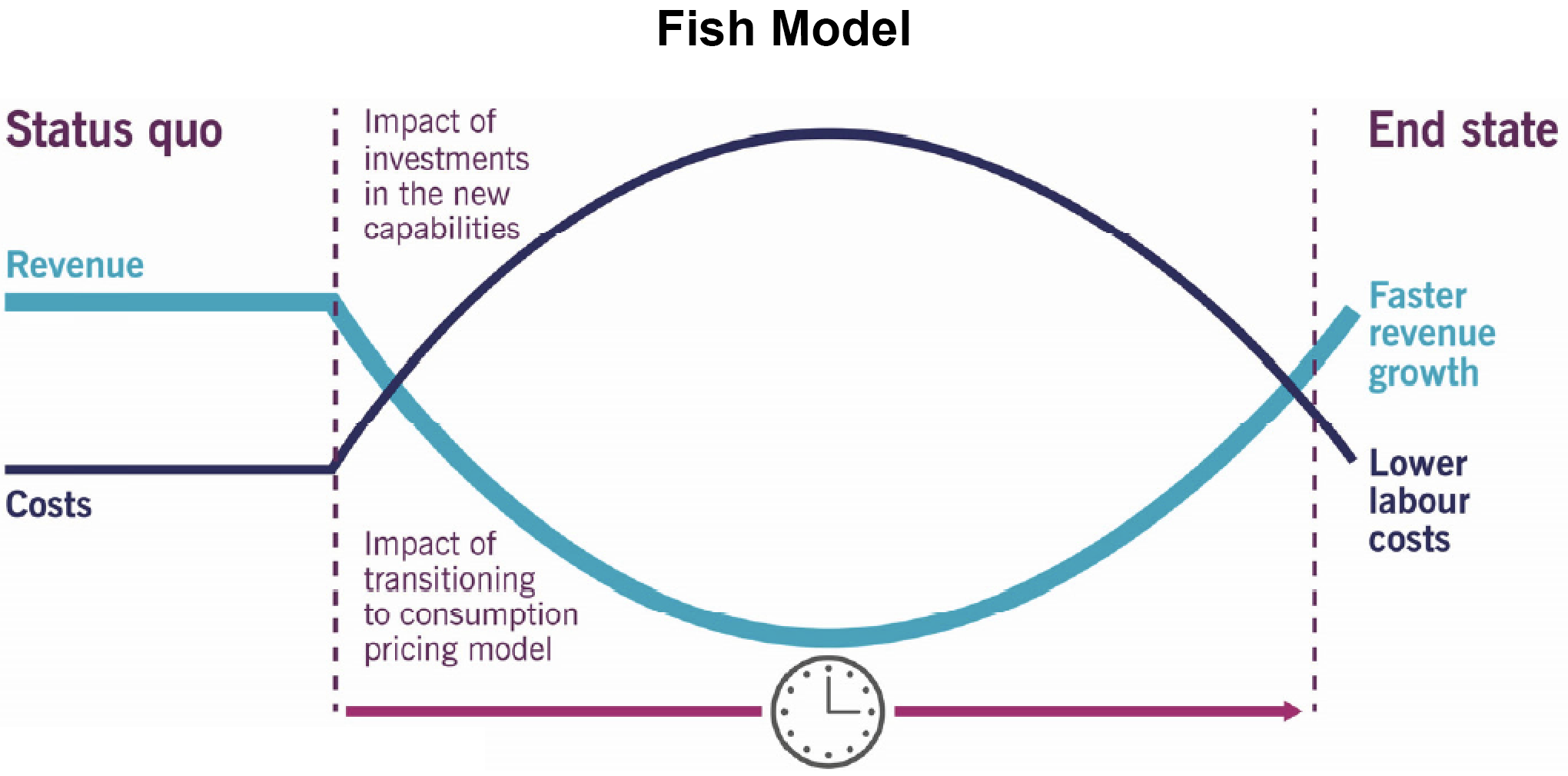
- Moving from capital to operational expenditure models:
- Causing organizations to drive cloud adoption and migration
- Funding via operational expenses allows more flexibility and speed to change solutions
- Leading to growth in subscription-based services (Fish Model), such as Adobe Creative Cloud as opposed to license purchases
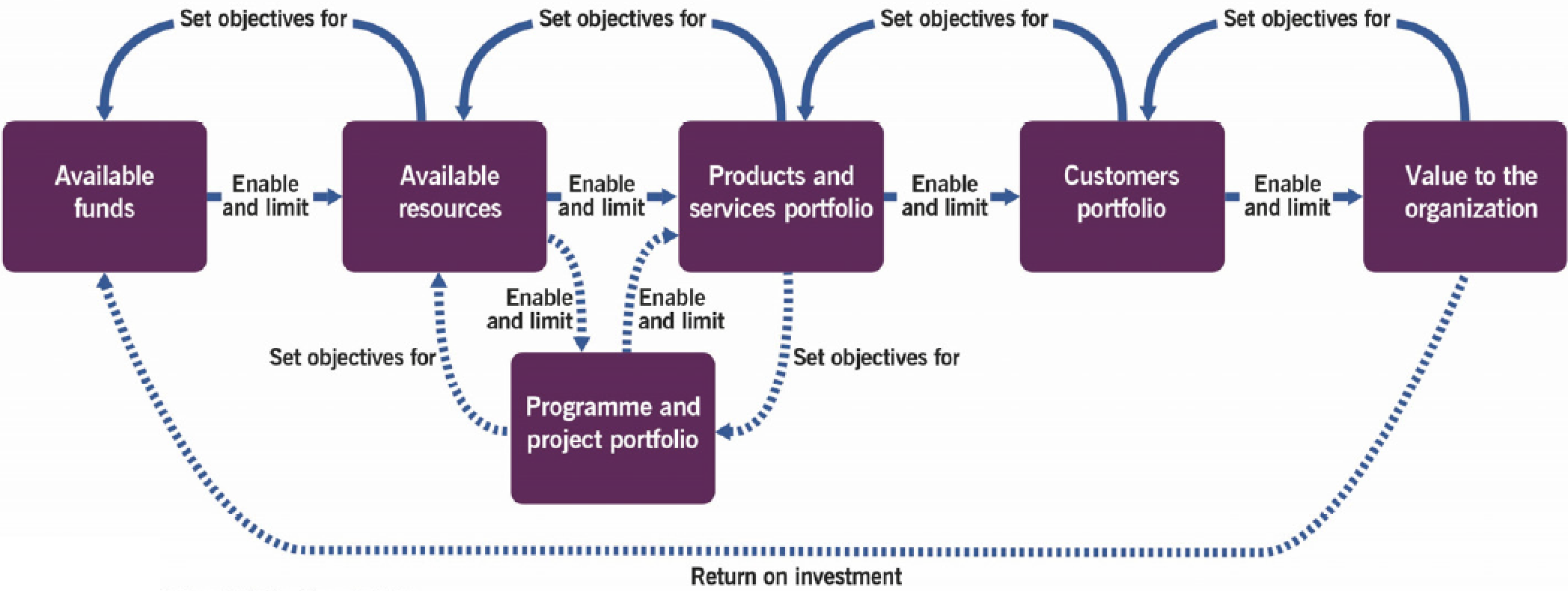
2. Portfolio optimization
Portfolio: a collection of assets into which an organization chooses to invest its resources in order to receive the best return
Portfolio types:
- Product and service portfolio: represents the commitments and investments by the provider for customers/market spaces
- Program and project portfolio: manage and coordinate projects, ensuring deadlines are met, maintain budget and scope. Ensures non-duplication
- Customer portfolio: commitment to serve customer groups and market spaces; may influence product/service portfolio; maintain relationship between business outcomes, customers, services are understood
Use the portfolios to track investments across lifecycle, link investment to anticipated value proposition: strategic tool for informed decision-making to balance investment of new and existing products/services
3. Funding projects, products, services
Not all projects are strategic and require funding beyond the operating budget:
- Replacing technology without performance/quality hit
- Moving non-compliant components into compliance
Must have a policy within financial strategy to support the non-strategic project
4. Balancing cost of innovation and operation
Traditionally, innovation is separated from operations. If there is an innovation initiative, staff moved from ops to the innovation team and then moved back when the innovation project completes
Agile organizations need to recognize innovation is part of their culture and ongoing business practices. Every operational budget and employee objective should have some level of innovation
Full cost recover models (working capital fund):
- Operating expense recovered from internal and external customers; maintains operations but also drives innovation
- Benefits:
- Improves transparency
- Drives strategic investment planning
- Reduces funding fluctuation
- Consider:
- Good demand forecasting
- Automated reporting
- Sufficient contingency plan
5. Charging models
Many strategies can be used to determine pricing. For existing products/services, must be competitive and will show cost, price, profitability
Must consider long-term pricing impacts in a digital age – competitors will quickly create the same products/services – must have a level of flexibility and a policy around profits and margins
For services offered internally, have a policy that makes the cost of technology transparent:
- Keeps service costs low
- Improvement is easy to understand
- Keeps consumer prices low
Digital charging models:
| Type | Description |
| Free | Offer a free-to-use product or service that is supported by other forms of revenue, such as advertising or referral/affiliate |
| Freemium | Offer a free-to-use product or service that is supplemented by additional paid packages |
| Tiered | Offer different packages with increasing levels of features at different price points |
| Dynamic/variable | Seven types of dynamic pricing are shown |
Go back to ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Customer/Market Relevance to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course.
Interesting Topics
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Managing Professional
Study, study and study, I couldn’t be successfully certified without studying it, if you are interested...
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Strategic Leader
With my ITIL 4 Managing Professional certification (ITIL MP) in the pocket, it was time to go for the...
-

Hide visual and change background color based on selection
Some small tricks to customize the background colour of a text box...
-

Stacked and clustered column chart or double stacked column chart
In excel, I use a lot the combination of clustered and stacked chart...
-

Refresh Power BI
From the Power BI Service, I can set refresh but, for instance, there is no option to do it monthly or each time a change is made...
-

Power BI alerts to be sent by email from an excel file based on condition
I will explain how to send a list of emails from an excel file after creating alerts...