ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Environmental Analysis
To begin this course, go to the main page ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course.
2. Environmental analysis
Strategy articulates the past, current, and future relationships between an organization and its environment. Three areas:
- External environment (outside the organization): PESTLE
- Internal environment (within the organization): four dimensions
- Interaction between the two
1. External analysis
Porter’s Five Forces: competitive dynamics in an environment (competition, new entrants, power of suppliers, power of customers, threat of substitute products)
With external analysis, strategy asks:
- What needs exist in our environment ?
- How important are those needs to people and other organizations ?
- How could those needs be fulfilled? What products/services meet that need ?
- How do those needs change over time ?
- Are other organizations meeting those needs? Is it adequate ?
- What are the limitations of our environment? Are we prevented from doing anything ?
1.1 PESTLE
Categorizes factors influencing/constraining how an organization operates:
| Factors | Description | Examples |
| Political | The influence of governments through policies (tax, fiscal, trade, labor, state ownership and so on), stability, level of corruption, openness to influence, available subsidies, and so on | Governments may force or ban the use of certain technology platforms or applications |
| Economic | Factors determining performance of an economy, such as inflation, interest rates, foreign exchange rates, demand/supply models, foreign investment, unemployment rates, and consumer purchasing power | Economic fluctuations may affect affordability of consumer technologies; commoditization and adoption of technology solutions are closely related to the costs of provision and consumption |
| Social | population’s culture, attitudes, norms, values, demographics (such as age, income, location, language), buying trends, mobility, and so on | Social movements for or against certain technology solutions, their vendors, or even countries of origin may change the technology adoption overnight |
| Technological | The level and impact of technology innovation, including focus on research and development, attitude to innovation and technology, incentives to use innovative technology, automation, and so on | Technology innovations affect existing solutions, sometimes by quickly replacing them completely |
| Legal | Related to political, but specifically legislation rather than policy, including laws related to discrimination, competition, employment, consumer protection, copyright and patents, and health and safety | Legislation regulating data processing, privacy and other information-related matters may limit, prohibit, or endorse adoption and development of certain technologies |
| Environmental | Constraints or enablers related to the availability (or scarcity) of natural resources, geography, climate, pollution, and carbon footprint targets | Environmental factors, especially of disastrous type, may interrupt or stimulate operation and adoption of certain technology |
1.2 Tools
| Tool | Description | Use |
| PESTLE | A framework to analyze macroenvironmental factors that impact an organization | Monitoring impact and potential changes to the organization so that it can adjust its position or strategy to stay relevant |
| SWOT Analysis | A tool to analyze the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing an organization | To identify actions an organization must take, relative to a specific opportunity or situation |
| Delphi method or estimate/talk/estimate | A forecasting process framework where several rounds of questionnaires are sent to a group of experts and shared with the group after each round | Forecast the results of a proposed action or scenario, and determine the best course of action or response |
| Lifecycle analysis | A method used to evaluate the environmental impact of a product through its lifecycle | To determine what standards must be met to compete in an ecologically sensitive market, and how to comply with them |
| Scenario planning | A method where variables in a market or situation are described, and results are projected for alterations of each variable | To understand the range of outcomes that might result in a situation in the organization’s environment, understand what causes them, and develop a plan for each likely outcome that is adjusted as more certainty about the variables is learned |
| Value ecosystem analysis or business ecosystem analysis | A method used to map the different parts of a business ecosystem and the value that they contribute and derive from each other | Create detailed business or operating models, and evaluate the impact of changes in the environment on the value of the relationships between ecosystem components |
| Porter’s Five Forces | A framework for evaluating competitive forces/dynamics operating in an environment; these are:
|
Analysis of an organization’s value proposition and how to strengthen its competitive position in situations influenced by various types of competitor |
| Directional policy matrix | A tool to identify preferred market segments based on how attractive the segment is and whether the organization has the capabilities to support it | Market segmentation, especially when identifying markets for existing capabilities; also helps to identify what capabilities need to be developed in pursuing a market segment |
| Competitor analysis | A method of analysing a specific competitor’s products, sales methods, sourcing and manufacturing methods, and marketing strategies | Create strategies that are designed to improve an organization’s capabilities to make them better than a competitor’s, to outperform it in the market |
2. Internal analysis
Once external impact is known, look internally; look for ways that the organization succeeds in its environment
Internal analysis determines:
- Whether the organization has the capabilities required to achieve its purpose in the environment that it operates in
- Whether current capabilities could be used to create new lines of business, products, or services
- Where it might be possible to make the organization more effective or efficient in meeting its purpose
With internal analysis, strategy asks:
- What capabilities do we need to fulfil the identified needs ?
- What knowledge would we need ?
- Which people would we need to hire ?
- What technology would we need to invest in ?
- What unique characteristics does the organization have that enable it to fulfil needs in a way that cannot be easily copied by competitors?
- Would we need to work with other organizations ?
- What are our constraints ? What are we unable to do, or what are we able to do in one way but not in another way ?
- How should we organize ourselves ?
- What is the best way of working to fulfil the identified needs ?
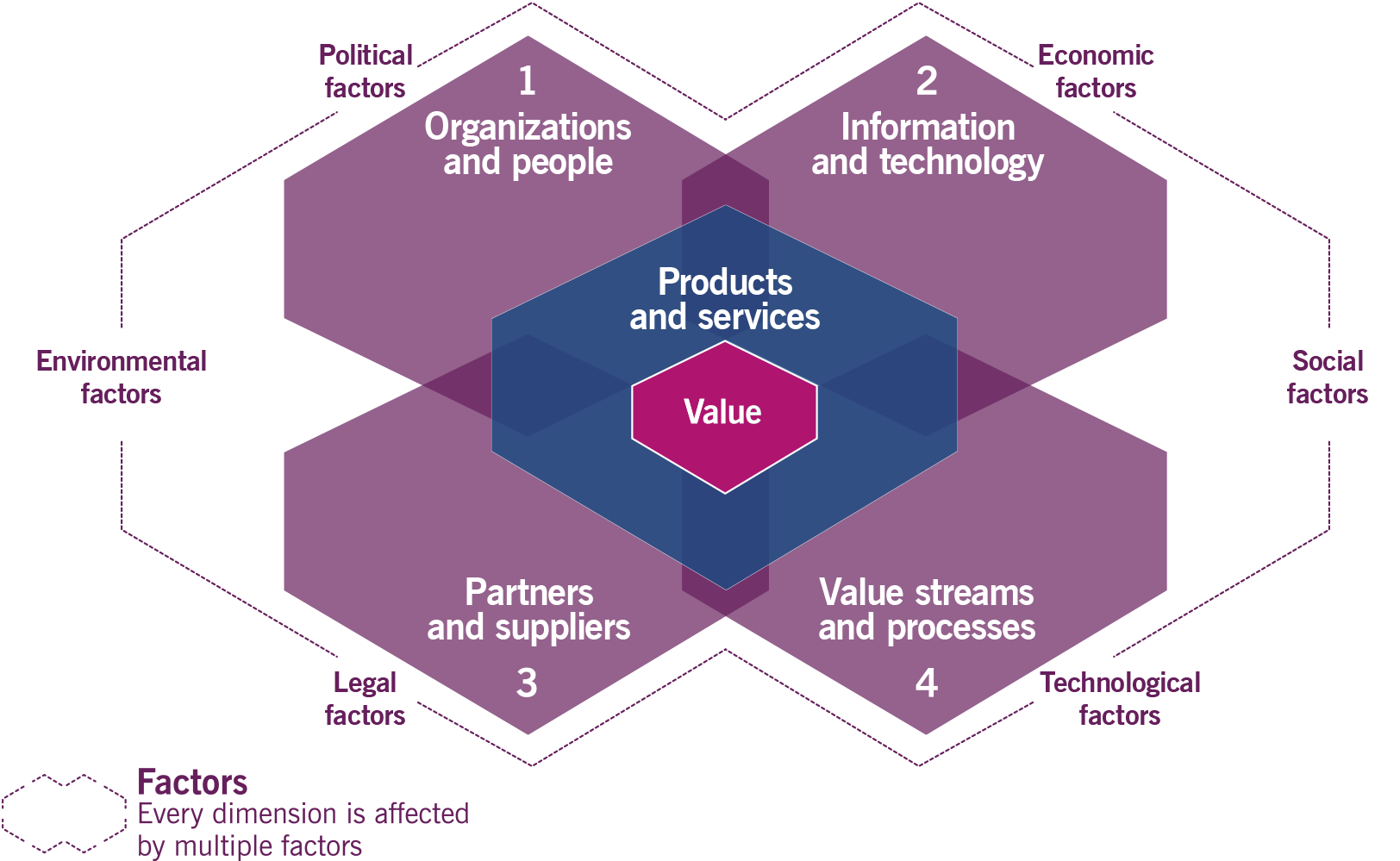
Internal environment is the four dimensions which describe organizational resources and how the interact with each other
2.1 Four dimensions
| Dimension | Description | Examples |
| Organizations and people | The organization’s structure and system of authority Skills, knowledge, and competency of its workforce Leadership that supports the organization’s values Organizational culture The ability to collaborate and coordinate across areas of specialization Clear definition of roles and responsibilities |
The organization’s culture, competencies and structure are critical for a digital strategy, and define its overall attitude towards digital technology |
| Information and technology | The systems, information, knowledge, and experience required to make good decisions and follow them Automation of activities and decisions The means to create value Together with people and partners, the means to build and deliver products and services How information is exchanged between different parts of the organization and its partners The design, procurement, or building of technology Which technology best suits the organization’s needs… |
Current technology architecture, including automation and digitization of the business, define a starting point, opportunities, and constraints for the digital strategy |
| Partners and suppliers | Those that supply goods or services that enable an organization to create value, and to build, sell, and deliver products and services Deciding whether to manufacture tools or perform activities internally, or to source them from a supplier or partner How contracts are negotiated, agreed, and managed How supplier and partner performance is aligned to the organization’s objectives How supplier and partner performance is measured and reported |
Opportunities and constraints for the organization’s digital strategy are defined by its dependency on third-party technology and by the digital strategies of its key partners and suppliers |
| Value streams and processes | What activities, workflows, controls, and procedures are needed to achieve the organization’s objectives Which products and services are produced, what steps are taken to produce them, and how much those steps cost The cost and return of each product and service Delivery models for each product or service |
The levels of automation and digitization of the organization’s value streams, together with the complexity and variability of processes and workflows, impact the objectives of the digital strategy and provide opportunities and constraints for it |
2.2 Tools
| Tool | Description | Use |
| SWOT analysis | A tool to analyse the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing an organization | To compare an organization’s strengths and weaknesses with the capabilities required to exploit opportunities and reduce threats; used to identify threat countermeasures, and to identify which capabilities need to be developed |
| Delphi method or estimate/talk/estimate | A forecasting process framework where several rounds of questionnaires are sent to a group of experts and shared with the group after each round | Can be used internally to determine what course of action to take to improve the organization or deal with a challenge |
| Lifecycle analysis | A method used to evaluate the environmental impact of a product through its lifecycle | To create policies about how to produce the most responsible design and manufacturing, packaging, and distribution methods for a product |
| Scenario planning | A method where variables in a market or situation are described, and results are projected for alterations of each variable | To understand the range of outcomes that might result in a situation of organization change, understand what causes them, and develop a plan for each likely outcome that is adjusted after developing greater certainty about the variables |
| Value ecosystem analysis or business ecosystem analysis | A method used to map the different parts of a business ecosystem and the value that they contribute and derive from each other | Creating detailed business or operating models, and evaluating the impact of changes in the environment on the value of the relationships between ecosystem components |
| Skills matrix | Assessment techniques used to identify the type and level of skill and knowledge in an organization | Determining whether the current profile of skills and knowledge is enough to embark on a particular course of action; identifying the needs for training and education programs |
| Capability maturity matrix | A maturity model, applied in many contexts, that rates an organization’s maturity relative to an industry approach or standard | To determine how proficient an organization is in a specific area (e.g. software engineering, service management, security and risk management) |
| Cultural assessments | Assessments that determine the way in which work is performed, decisions are made, risks are taken, innovation is encouraged, etc. | Cultural assessments can help in preparing for the required changes, and determining how to best promote them within the organization |
3. Interaction between organization and environment
Environmental analysis goes beyond strategy definition:
- Changes occur (jobs created/removed, products/services delivered, managed resources and their consumption…)
- All changes are not easy to predict, must continuously monitor and analyze the organization and its environment:
- How the needs being met by the organization are changing
- Who is competing to meet those needs
- Whether there are new, better ways of meeting them
- Whether the size of the existing needs is changing (increasing or decreasing)
- Whether new needs are emerging
- Whether the organization’s services and products are still adequate to meet needs in the environment, and if not, how they will need to change
- Whether new capabilities have evolved that will change the organization’s business model
4. Using environmental analysis results
Environment analysis helps the organization to identify and articulate:
- The purpose of the organization
- The nature of its interactions with its environment
- The products and services it offers, and the needs that each one fulfils
- The size of the needs it will fulfill
- The constraints imposed by its environment
- The capabilities it will need
- How it will organize itself to fulfil its purpose (e.g. its business model)
- Who it will need to cooperate with
Go back to ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course for the other chapters if you completed this Environmental Analysis chapter.
Interesting Topics
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Managing Professional
Study, study and study, I couldn’t be successfully certified without studying it, if you are interested...
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Strategic Leader
With my ITIL 4 Managing Professional certification (ITIL MP) in the pocket, it was time to go for the...
-

Hide visual and change background color based on selection
Some small tricks to customize the background colour of a text box...
-

Stacked and clustered column chart or double stacked column chart
In excel, I use a lot the combination of clustered and stacked chart...