ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Implementing a Digital Strategy - Assessing the Success of DITS
Metric: measurement or calculation that is monitored or reported for management and improvement
Indicator: metric that is used to assess and manage something
Key performance indicator: important metric that is used to evaluate the success in meeting an objective
Performance: measure of what is achieved or delivered by a system, person, team, practice, or service
Measurement is just one aid to successful management, consider leadership, communication, design, intuition…
Why measure:
- Influence behavior
- Justify change
- Validate decisions
- Intervene
Measurement categories:
- Performance
- Maturity
- Compliance
1. Metric types
Effectiveness: degree to which an activity (or group of activities) fulfills purpose and achieves objectives
Efficiency: how resources are utilized to perform activities and manage products/services
Productivity: show amount of work performed and resulting outputs (throughput of a resource or system)
Conformance: how managed object meets pre-agreed rules and requirements
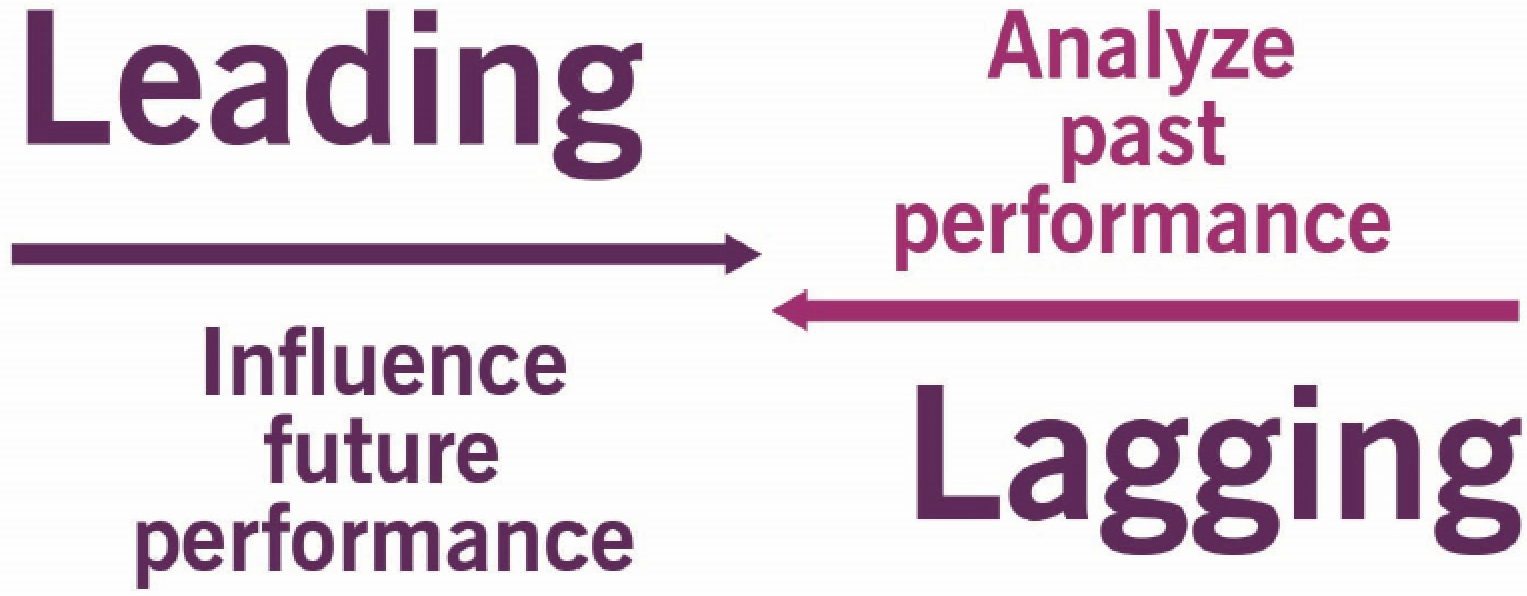
2. Lagging and leading metrics
3. Outside-in and inside-out metrics
Outside-in:
- Customer view of the organization’s services
- Use to drive priorities and actions to meet customer needs
- Customer reports should be based on outsidein metrics highlighting the value and outcomes achieved that the customer wants
Inside-out:
- Internal organizational view of services
- Can be a constraint when used to force customers to comply with the way the organization works, rather than changing the way the organization works to meet the customer need
4. Metrics and indicators
Metrics useful when used to support decisions by indicating something important:
- They become indicators -> key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Metric is a KPI when it’s crucial for assessing an object’s state (good, bad, acceptable…): must have an agreed target value and tolerance range
Using metrics as KPIs:
- Identify key metrics
- Define target values, trends
- Define tolerance (range of performance)
5. Cascading/linking measurements
Understand that different audiences need to see the metrics that allow them to measure and change. Different metrics for the same thing may be needed to fit the individual needs
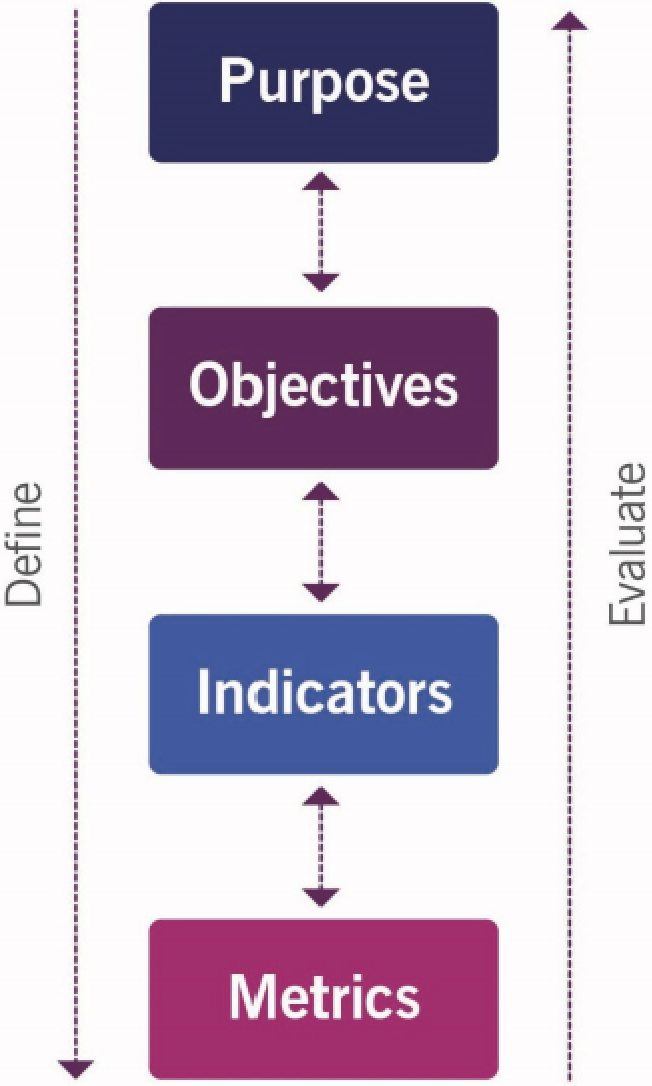
6. Metric examples
| Focus | Purpose | Objectives | Indicators | Metrics |
| Strategy | The purpose of the organization defining the strategy | Strategic objectives, such as ability to operate in a particular market or grow a particular line of business | Outcome-based | Organizational achievements (such as revenue growth level attained, market share), benchmark results |
| Strategic initiative | To implement an aspect of the organization’s strategy (e.g. build a new product, create a new customer engagement model) | Project objectives, such as time to complete, budget, specifications | Achievement-based | Milestones met, money spent, resource utilization, specifications complied with |
| Function/department or team operations | To use the resources, tools, processes, etc. defined by the organization to perform the roles assigned to them (e.g. manufacture products, sell products) | Operational objectives, such as work rates, production levels, output quality | Performance-based | Revenue generated, expenses, productivity (quantity, quality, and timing), audits |
| Order/service request/incident/change/etc. | To identify, process, and complete items of work assigned to a function, team etc. | Process objectives, such as ticket duration, quantity, frequency, maximum cost | Occurrence-based | Number completed, time to complete, cost per ticket, revenue per ticket, occurrence patterns |
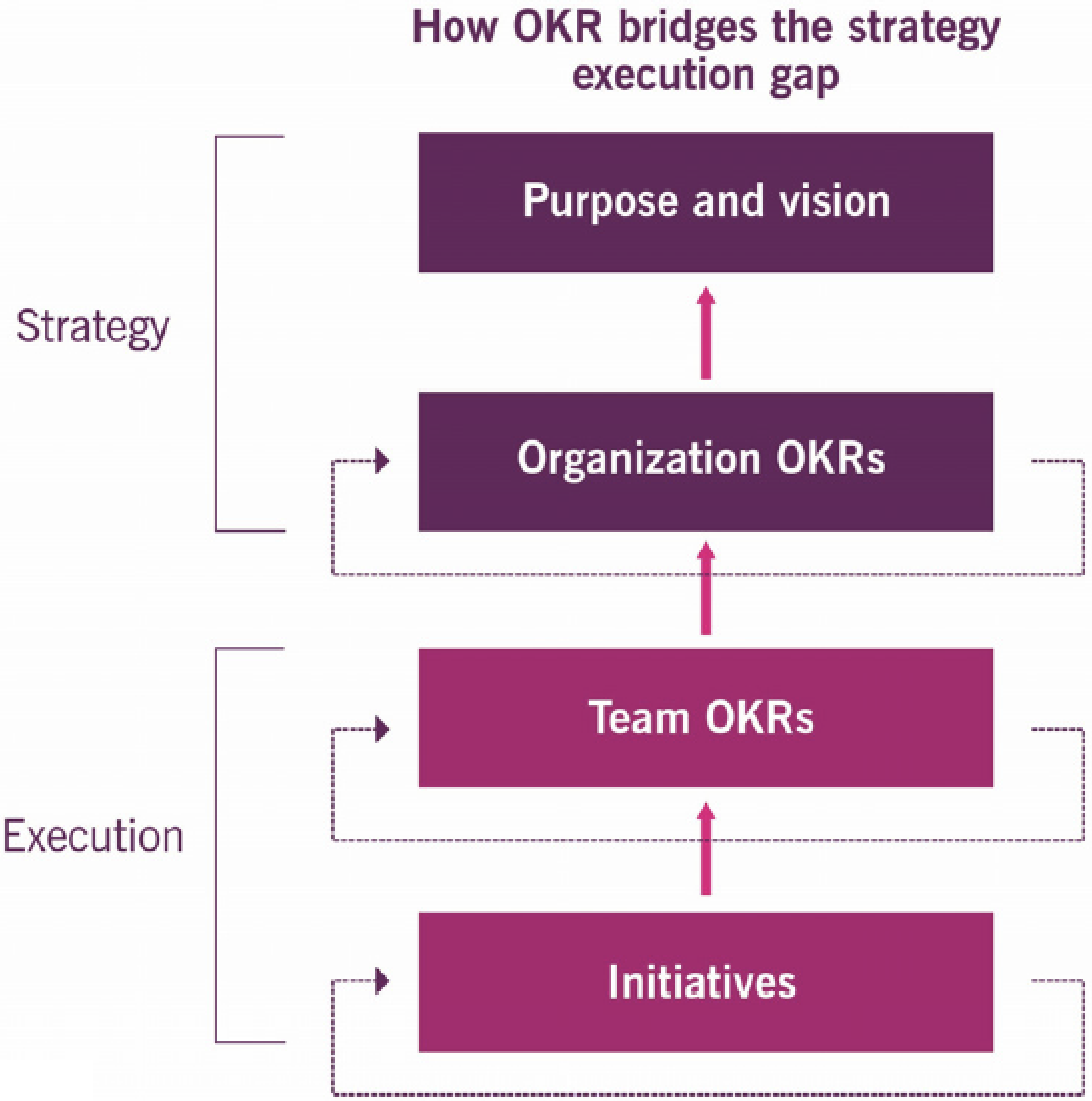
7. Objectives and key results (OKR)
Key message: a framework for defining and tracking objectives and their outcomes
Focused on defining strategic objectives and outcomes (what the organization does with their associated effects)
The successful achievement of an objective must provide clear value for the organization
Objectives are whats. They:
- Express goals and intents
- Are aggressive yet realistic
- Must be tangible, objective, and unambiguous; obvious that an objective has been achieved
Key results are hows. They:
- Express measurable milestones that, if achieved, will advance the objective(s)
- Must describe outcomes, not activities
- Must include evidence (available, credible, and easily discoverable) of completion
7.1 OKRs bridge strategy and execution
8. Measuring a strategy
Measurement frequency should match the organizational volatility (annual vs. quarterly vs. monthly)
Adjust and evolve existing strategy (guiding principle: start where you are)
Budgeting policies must link with strategy cycle, must meet financial reporting requirements as well as the changing demands of strategic initiatives and the potential for changed operations
Align operational reports to the strategic report (easier to see impact of a strategy)
Why measure a strategy ?:
- Has it been implemented as planned (progress) ?
- Is it achieving its defined objectives (performance) ?
- Is it still relevant/suitable given changes in the internal or external environment (relevance) ?
8.1 Measuring progress
Are strategic initiatives proceeding on time, to specification and to budget ?
If there is a deviation, leaders can:
- Allocate additional funding to an initiative
- Revise the timelines of the strategy
- Alert key stakeholders of delays (or acceleration) to the delivery of a particular outcome
- Decide on whether to continue with the initiative or switch to an alternative
- Adjust the strategy as appropriate
8.2 Measuring performance
All initiatives are on track but is the strategy still meeting its objectives ?
If there is a deviation, leaders can:
- Change the strategy to respond to a particular event (delaying one new product line while doubling efforts to launch another on time)
- Move to implementing an alternative scenario
- Allocate additional resources to one part of the organization
- Withdraw from an opportunity or market (cancels that part of the strategy)
8.3 Measuring relevance
Are initiatives progressing to plan ? Is the strategy meeting its stated objectives ? Even if the answer is yes, internal/external environmental changes can quickly impact that success and RELEVANCE
Determine via regular strategy reviews: volatility of the market determines the frequency of the review
Realize the strategy itself the causes changes. During the review, focus on environment changes that are independent of the strategy as well as the cause-and-effect relationships within the strategy
A strategy that is no longer relevant is not viable, regardless of how well it was implemented. Every review cycle should evaluate whether the effect of the strategy was as intended
9. Instrumenting strategy
Collected information (data) is typically used for reports but also useful:
- Audits
- Quality management
- Continual improvement
- Service validation
Metrics used should be relevant to the recipient and presented in a manner that easy to use/understand
Reports contain measurements but also outputs. Comparisons between actual and target values (highlight deviations), actual and previous performance (trends), different indicators (evaluate correlations, identify bottlenecks)
Reports are operational or analytical
10. Operational reports/dashboards
Operational reports identify deviations from plans/objectives as they happen which allow quick corrective action:
- Typically automated, reports are fact-based, so little human interaction needed
- Can be delivered often, ensures best information is used to support decisions
Dashboards report but:
- Present only important indicators
- Displays information on a single screen
- Available online
- Real time updates (or close to it, as agreed)
11. Analytical reports
Identifies hidden issues, defines causes, discovers improvement opportunities
Understands facts to deliver conclusions and recommendations
Full automation is not possible
Requires analyst and time
Report is typically printed and may require release authorization
12. Operational vs. analytic reports
| Property | Operational report | Analytical report |
| Purpose | To deliver information to evaluate the current state, to identify bottlenecks, and to support operational decisions |
To deliver analytical evaluation of the managed object, to identify hidden issues and their causes, and to suggest improvement options |
| Activity to produce | Ongoing measurements of resources and operations |
Targeted analytical research |
| Content | Measurement results Comparisons with the target and historic values Matching different indicator values to identify correlations and bottlenecks |
Content is driven by the research goal and analysis method; a sample table of contents can be as follows:
|
| Production technology | Automated, with minimal human labor |
Manually created by a qualified analyst; such a report requires both data collection and human involvement in the form of interviews, workshops, and brainstorming |
| Production time | From several seconds to several hours |
From several days to several months |
| Decision horizon | Not exceeding a quarter; normally within a month |
From a quarter to several years |
| Authorization | Not required |
Sometimes required |
13. Strategy review
Purpose: to ensure the ongoing relevance and effectiveness of strategy
Every strategic cycle contains a review step. Optimize the initiative fulfillment within defined/agreed scope
Review should examine the impact of the metrics that have been defined for the previous cycle, specifically to detect unintended consequences (metrics shouldn’t influence behavior to deliver unintended results)
Data provides a basis for review, but means little without insight (insight: ability to gain an accurate and deep understanding of the situation):
- Result of intelligence, emotions, experience, feelings
- ALOE (ask, listen, observe, empathize) and development of emotional, social and system intelligence support an organization’s performance and evolution
Go back to ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Implementing a Digital Strategy to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course.
Interesting Topics
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Managing Professional
Study, study and study, I couldn’t be successfully certified without studying it, if you are interested...
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Strategic Leader
With my ITIL 4 Managing Professional certification (ITIL MP) in the pocket, it was time to go for the...
-

Hide visual and change background color based on selection
Some small tricks to customize the background colour of a text box...
-

Stacked and clustered column chart or double stacked column chart
In excel, I use a lot the combination of clustered and stacked chart...
-

Refresh Power BI
From the Power BI Service, I can set refresh but, for instance, there is no option to do it monthly or each time a change is made...
-

Power BI alerts to be sent by email from an excel file based on condition
I will explain how to send a list of emails from an excel file after creating alerts...