ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Risk and Opportunities - Encouraging and Managing Innovation
Innovation: the adoption of a novel technology or way of working that has led to the significant improvement of an organization, product, or service
Innovation only takes place if an idea has been implemented and it has impacted the organization
Innovation can be used to determine the strategic position
Innovation does not just make new capabilities and efficiencies available to organizations, it changes the fundamental nature an organization’s external and internal environments
Other innovation will improve the efficiency or effectiveness of existing activities (outperforms competitors offering similar products or services)
Successful digital organizations must, at the very least, be able to track, adopt and adapt these innovations to be able to maintain their position
To grow their competitive advantage, they must become innovative themselves
1. Innovation as a strategic capability
Manage innovation to enable the organization to succeed in a volatile environment
Innovation is used to:
- Determine organization’s strategic position
- Improve performance (effectiveness, efficiency) so to outperform competitors
- Challenge existing strategies and objectives
Digital leadership uses innovation deliberately: chose what will best meet the needs of the organization to achieve desired outcomes (success). Not all innovations are necessary, needed, valuable, etc.
2. Innovation as a strategic capability
Innovation is only valuable if it solves a customer problem
Innovation comes from organization’s R&D or innovation team – not exclusively true. Most innovation comes from entrepreneurs as their focus is on what’s important and not just interesting (solve customer problems, address customer needs)
Where do the best ideas come from ?
- Front-line workers (they see the struggles and frustrations of customers)
- Capture the information and ideas
3. Balanced approach to innovation
Innovation has rewards but comes with risks and it can be disruptive. Uncontrolled innovation is wasteful and potentially chaotic
To manage innovation, must manage uncertainty. Don’t know costs, returns, if it will work, if it will be accepted
Must develop an innovation posture (similar to a risk posture). How an organization will respond to:
- Overall driver
- Ability to tolerate disruption
- Innovation intensity
- Strategic alignment
- Return on investment
- Leverage
- Risk appetite
- Incentive to innovate
4. Innovation management
Innovation is characterized by uncertainty, risk, and complexity: manage with formal flexibility (have a structure and methodology but allow for exceptions)
Organizing innovation management:
- Centralized team of management supported by subject matter experts (SMEs) who do the actual work
- Will report to senior executive to maintain alignment with strategy
- Innovation should expand beyond these teams; have clear guidance for managers to encourage and coordinate innovative ideas/actions
Managing innovation activities:
- Collective process; must have a shared sense of purpose
- Cultivate a climate for open communication, sharing of ideas, trust…creates a strong innovation culture
- Must be able to capture and evaluate each idea to the kill or progress stage; work purposefully (not to fast) for optimal results
5. Steps in managing innovation
Generate and capture ideas: brainstorm, design thinking, innovation fairs, hackathons…
Filter ideas: will it ‘help’ the customer; is it needed ?
Incubate ideas: moves an idea from a concept to reality
Evaluate ideas: use established criteria (costs, return, business need…) to accept or reject the idea (executives should set the criteria as well as evaluate)
Select ideas: base selection evaluation ranking and potential to address challenge
Identify/charter a team to build/test: consider proposer, tech experts, architects, project management, organizational component experts
Develop prototypes: several rounds of development begins with a prototype (viability, reasonable…)
Design, develop, test: work from an accepted prototype following CDS concepts (value stream)
6. Technology adoption lifecycle
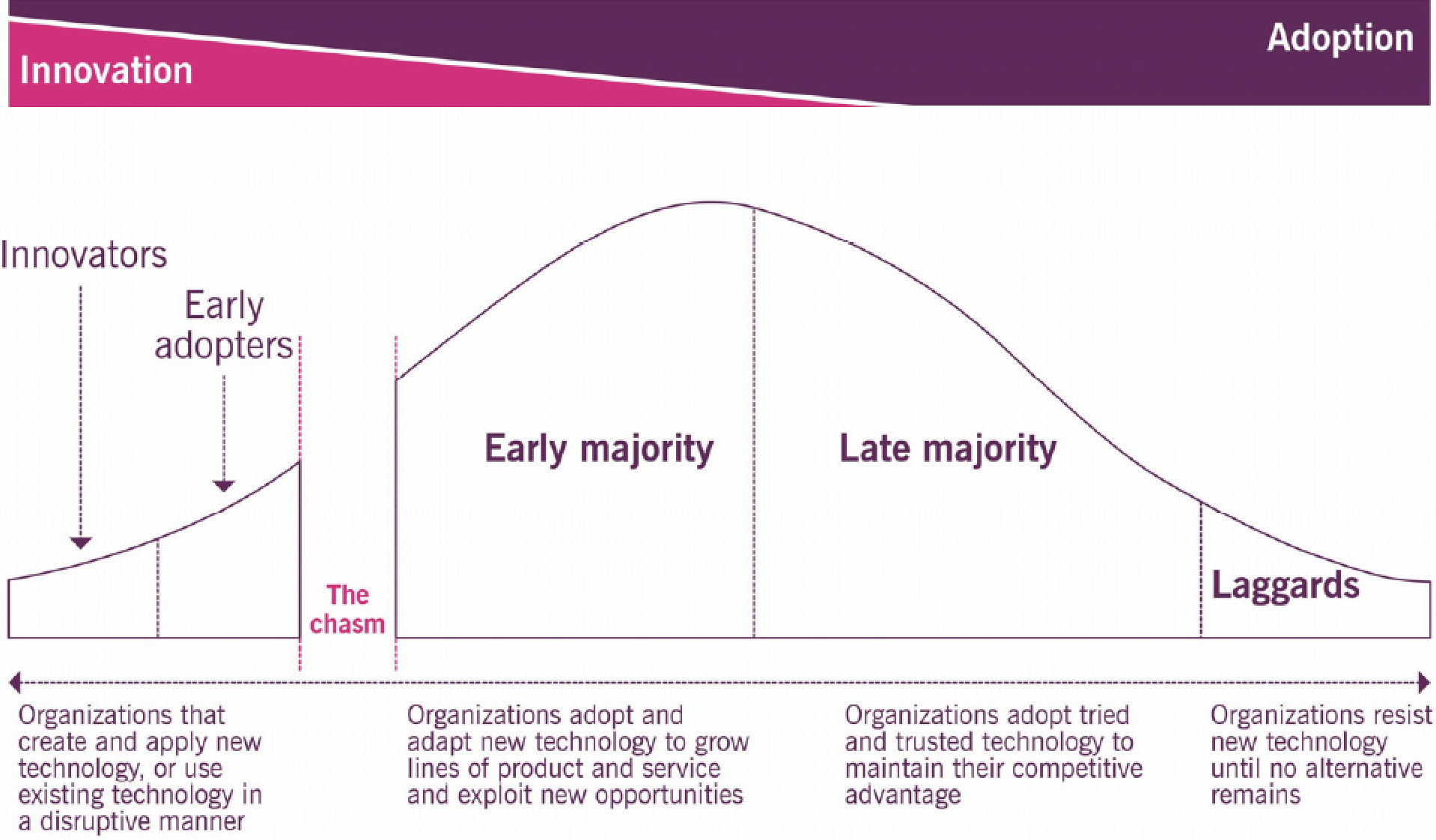
7. Evaluate and adopt emerging technology Ask:
Stages of technology adoption:
|
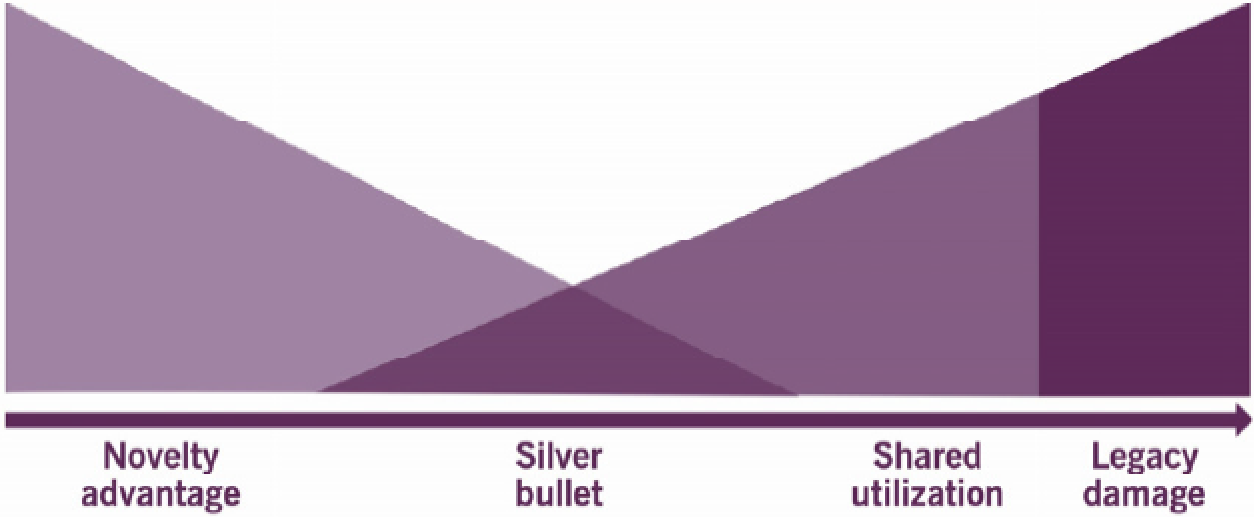 |
8. Emerging technology in context
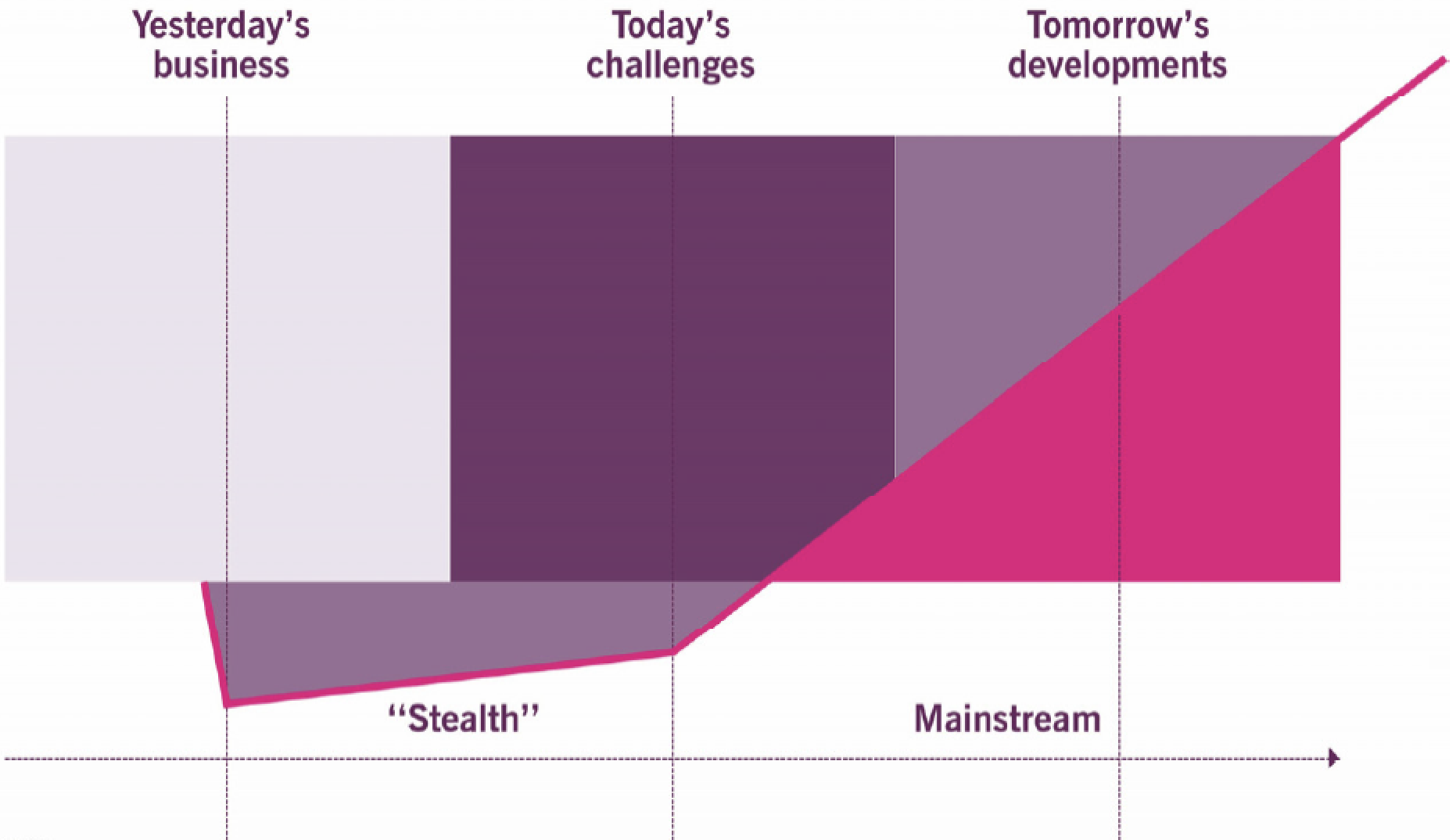
9. Building an innovation-supporting culture
It is a process, consider the following:
- Educate executives
- Work with workforce and talent management
- Evangelize digital technology opportunities
- Provide learning tools
- Give employees time to train, learn, and job-shadow
- Give employees the freedom to experiment
- Encourage teams to incorporate learning into every day
- Establish a market intelligence practice
10. Approaches to innovation
Managed chaos and distributed experimentation:
- Theory that suggests organizations are most successful when they adopt a volatile environment, empower employees and leaders, rely on self-organizing teams
- Rather than a root-cause focus, look at big picture patterns that foster or inhibit behaviors
- Fractal organization
- Formal R&D departments are viewed as progress bottlenecks
Difficult to adopt as most well-established organizations are command-control systems, with a top-down hierarchy:
- Not management-by-crisis
- Managed chaos is not pure chaos
Executive is the visionary, parameter-setter, enabler (mid-level leaders are coaches)
Transition to managed chaos by:
- Set the vision for innovation
- Hire curious employees
- Allow experimentation across the organization (legal and ethical)
- Define success metrics; data and results top opinion
Crowdsourcing:
- Sourcing model in which individuals or organizations obtain goods and services, including ideas, voting, micro-tasks and finances, from a large, relatively open and often rapidly evolving group of participants
- Typically initiated via contests
- Why do heavily invested R&D departments filled with exceptional scientists, engineers, developers do not create solutions that resonate with customer ? R&D (internal employees) threatened by crowdsourcing
To pursue crowdsourcing:
- Redefine the role of R&D
- Be specific in defining the problem
- Design appropriate rewards
- Understand intellectual property and ownership implications
Go back to ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Risk and Opportunities to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course.
Interesting Topics
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Managing Professional
Study, study and study, I couldn’t be successfully certified without studying it, if you are interested...
-

Be successfully certified ITIL 4 Strategic Leader
With my ITIL 4 Managing Professional certification (ITIL MP) in the pocket, it was time to go for the...
-

Hide visual and change background color based on selection
Some small tricks to customize the background colour of a text box...
-

Stacked and clustered column chart or double stacked column chart
In excel, I use a lot the combination of clustered and stacked chart...